The Federal Vacancy Count 11/30/2016
| ||||||||||
| ||||||||||
November 30, 2016
By Kevin Eirich
This month's Federal Vacancy Count includes nominations, confirmations, and vacancies from October 27, 2016, to November 30, 2016. Nominations, confirmations, and vacancies occurring on December 1, 2016, will be reflected in the December 2016 report.[1]
The vacancy warning level remained at yellow this month after four new vacancies were announced. The total vacancy percentage was 11.41 percent, and there were 111 vacancies out of 973 positions. There was one new nomination from President Barack Obama since the October 2016 update. The total number of nominees waiting for Senate confirmation is 66, including nominees to the United States Court of Federal Claims, the United States Tax Court, the United States Court of Appeals for the Armed Forces, and the Superior Court of the District of Columbia. The remaining 45 federal vacancies represent positions where a nominee has not been named by the president.
A breakdown of the vacancies at each level can be found in the table below. For a more detailed look at the vacancies on the federal courts, see Ballotpedia's Federal Court Vacancy Warning System. The Federal Court Vacancy Warning System presents information on current Article III judicial vacancies in the federal court system, as well as the status of pending nominees to the federal bench.
Vacancies by court
| Court | # of Seats | Vacancies |
| Supreme Court | 9 | 11.1% or 1 vacancy |
| Appeals Courts | 179 | 7.3% or 13 vacancies |
| District Courts | 677 | 12.25% or 83 vacancies |
| International Trade | 9 | 22.2% or 2 vacancies |
| Federal Claims | 16 | 37.5% or 6 vacancies |
| Tax Court | 19 | 10.5% or 2 vacancies |
| Armed Forces | 5 | 0% or 0 vacancies |
| D.C. Superior Court | 62 | 6.4% or 4 vacancies |
| All Judges | 973 | 11.41% or 111 vacancies |
New vacancies
The following judges vacated their active status on their respective courts, creating an Article III judicial vacancy. As Article III judicial positions, these vacancies must be filled by a nomination from the president. That nomination is subject to confirmation on the advice and consent of the U.S. Senate.
United States District Court for the District of Minnesota
| Donovan Frank is a federal judge on senior status with the United States District Court for the District of Minnesota. A native of Rochester, Minnesota, Frank graduated from Luther College with his bachelor's degree in 1973 and from the Hamline University School of Law with his J.D. in 1977. Frank was nominated by President Bill Clinton on May 21, 1998, to a seat vacated by Judge David Doty as Doty assumed senior status. The American Bar Association rated Frank Unanimously Qualified for the nomination. Hearings on Frank's nomination were held before the United States Senate Committee on the Judiciary on July 30, 1998, and his nomination was reported by U.S. Sen. Orrin Hatch (R-Utah) on September 17, 1998. Frank was confirmed on a voice vote of the U.S. Senate on October 21, 1998, and he received his commission the next day. Frank assumed senior status on the court on October 31, 2016. The current vacancy warning level of this court is orange. As of this report, the district court has two vacancies. Under current law, the court has a total of 7 active judicial positions.[2][3][4] |
|
United States District Court for the Northern District of Florida
| Robert Hinkle is a federal judge on senior status with the United States District Court for the Northern District of Florida. Born in Apalachicola, Florida, Hinkle graduated from Florida State University with his bachelor's degree in 1972 and from Harvard Law School with his J.D. in 1976. Hinkle was nominated to the United States District Court for the Northern District of Florida by President Bill Clinton on June 6, 1996, to a seat vacated by Judge William Stafford. The American Bar Association rated Hinkle Substantial Majority Well Qualified, Minority Qualified for the nomination. Hearings on Hinkle's nomination were held before the United States Senate Committee on the Judiciary on June 25, 1996, and his nomination was reported by U.S. Sen. Orrin Hatch (R-Utah) on June 27, 1996. Hinkle was confirmed on a voice vote of the U.S. Senate on July 25, 1996, and he received his commission on August 1, 1996. Hinkle served as chief judge of the district court from 2004 to 2009. He assumed senior status on November 7, 2016. The current vacancy warning level of this court is red. As of this report, the district court has two vacancies. Under current law, the court has a total of 4 active judicial positions.[5][6][7] |
|
United States District Court for the Central District of California
| Christina Snyder is a federal judge on senior status with the United States District Court for the Central District of California. A native of Los Angeles, California, Snyder earned her undergraduate degree from Pomona College in 1969 and her J.D. from Stanford Law School in 1972. Snyder was first nominated to the United States District Court for the Central District of California by President Bill Clinton on May 6, 1996, to a seat vacated by Judge Edward Rafeedie. The American Bar Association rated Snyder Unanimously Qualified for the nomination. Under Rule XXXI, paragraph six of the standing rules of the U.S. Senate, Snyder's nomination was returned to the president on October 4, 1996. President Clinton resubmitted Snyder's nomination on January 7, 1997. The American Bar Association again rated Snyder Unanimously Qualified for the nomination. Hearings on Snyder's nomination were held before the United States Senate Committee on the Judiciary on July 22, 1997, and her nomination was reported by U.S. Sen. Orrin Hatch (R-Utah) on September 18, 1997. Snyder was confirmed on a recorded 93-6 vote of the U.S. Senate on November 7, 1997, and she received her commission on November 10, 1997. She assumed senior status on November 23, 2016. The current vacancy warning level of this court is yellow. As of this report, the district court has four vacancies. Under current law, the court has a total of 28 active judicial positions.[8][9][10][11][12] |
|
United States District Court for the Eastern District of New York
| Carol Amon is a federal judge on senior status with the United States District Court for the Eastern District of New York. A native of Richmond, Virginia, Amon graduated from the College of William and Mary with her bachelor's degree in 1968 and from the University of Virginia School of Law with her J.D. in 1971. Amon was nominated by President George H.W. Bush on May 18, 1990, to a seat vacated by Judge Mark Costantino. The American Bar Association rated Amon Unanimously Well Qualified for the nomination. Hearings on Amon's nomination were held before the United States Senate Committee on the Judiciary on July 19, 1990, and her nomination was reported by then-U.S. Sen. Joseph Biden (D-Del.) on July 26, 1990. Amon was confirmed by the unanimous consent of the U.S. Senate on August 4, 1990, and she received her commission on August 7, 1990. From 2011 to 2016, she served as the chief judge of the district court. Amon assumed senior status on November 30, 2016. From 1986 to 1990, Amon served as a federal magistrate judge on the Eastern District of New York. The current vacancy warning level of this court is yellow. As of this report, the district court has three vacancies. Under current law, the court has a total of 15 active judicial positions.[13][14][15] |
|
New nominations
Superior Court of the District of Columbia
| Rainey Ransom Brandt is a magistrate judge on the Superior Court of the District of Columbia. She was sworn in as a magistrate judge on November 7, 2012. On November 15, 2016, President Barack Obama nominated Brandt to be an associate judge on the Superior Court. Brandt attended American University in Washington, D.C., where she earned her bachelor's degree in 1989, her master's degree in 1990, and her doctorate in 1993. She earned her J.D. from Catholic University of America in 1995. The president gave the following remarks on Brandt's nomination: "I am pleased to nominate Judge Rainey Ransom Brandt to serve on the Superior Court of the District of Columbia ... I am confident she will serve the District of Columbia with integrity and a steadfast commitment to justice." Brandt's nomination will be considered by the United States Senate Committee on Homeland Security and Governmental Affairs. The current vacancy warning level of this court is blue. As of this report, the Superior Court has four vacancies. Under current law, the court has a total of 62 active judicial positions.[16][17][18] |
|
New confirmations
There have been no new federal judicial confirmations by the U.S. Senate since our October 2016 update.
Monthly map
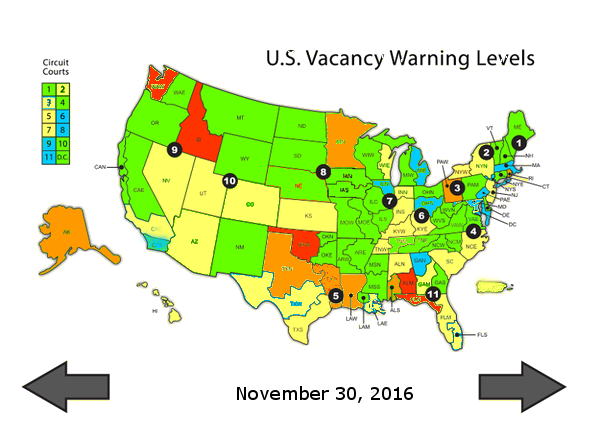 |
See also
- United States federal courts
- Federal Court Vacancy Warning System
- Supreme Court vacancy, 2016: An overview
Footnotes
- ↑ As of May 2016, Ballotpedia's Federal Vacancy Count includes nominees to the United States Court of Federal Claims, the United States Tax Court, the United States Court of Appeals for the Armed Forces, and the Superior Court of the District of Columbia. Vacancy, confirmation, and nomination totals will be changed accordingly. The map used in this report, however, does not include information from these courts at this time.
- ↑ Federal Judicial Center, "Biographical directory of federal judges," accessed November 3, 2016
- ↑ American Bar Association, "Ratings of Article III judicial nominees, 105th Congress," accessed November 3, 2016
- ↑ United States Congress, "PN 1113 — Donovan W. Frank — The Judiciary," accessed November 3, 2016
- ↑ Federal Judicial Center, "Biographical director of federal judges," accessed November 7, 2016
- ↑ American Bar Association, "Ratings of Article III judicial nominees, 104th Congress," accessed November 7, 2016
- ↑ United States Congress, "PN 1138 — Robert L. Hinkle — The Judiciary," accessed November 7, 2016
- ↑ Federal Judicial Center, "Biographical directory of federal judges," accessed November 17, 2016
- ↑ American Bar Association, "Ratings of Article III judicial nominees, 104th Congress," accessed November 17, 2016
- ↑ American Bar Association, "Ratings of Article III judicial nominees, 105th Congress," accessed November 17, 2016
- ↑ United States Congress, "PN 1095 — Christina A. Snyder — The Judiciary," accessed November 17, 2016
- ↑ United States Congress, "PN 22 — Christina A. Snyder — The Judiciary," accessed November 17, 2016
- ↑ Federal Judicial Center, "Biographical directory of federal judges," accessed November 30, 2016
- ↑ American Bar Association, "Ratings of Article III judicial nominees, 101st Congress," accessed November 30, 2016
- ↑ United States Congress, "PN 1289 — Carol Bagley Amon — The Judiciary," accessed November 30, 2016
- ↑ District of Columbia Courts, "Superior Court: Rainey R. Brandt," accessed November 18, 2016
- ↑ The White House, "President Obama nominates Judge Rainey Ransom Brandt to serve on the Superior Court of the District of Columbia," November 15, 2016
- ↑ The White House, "Presidential nomination sent to the Senate," November 15, 2016
| |||||







