Become part of the movement for unbiased, accessible election information. Donate today.
Judicial Branch: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
<div class="bp-layout-block"><h2 style="margin:0; background:#3149ab; color:white; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #C0C0C0; text-align:left; color: white; padding:0.2em 0.4em;"><font face=Helvetica>News headlines</font></h2> | <div class="bp-layout-block"><h2 style="margin:0; background:#3149ab; color:white; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #C0C0C0; text-align:left; color: white; padding:0.2em 0.4em;"><font face=Helvetica>News headlines</font></h2> | ||
<div style="margin-top:10px;"><DPL> | <div style="margin-top:10px;"><DPL> | ||
category = Federal court news, | category = Federal court news, 2020 | ||
count = 4 | count = 4 | ||
ordermethod = firstedit | ordermethod = firstedit | ||
Revision as of 17:22, 1 June 2020
History of the federal courts
|
The only court created by Article III of the United States Constitution was the Supreme Court of the United States. "Inferior courts," per Article III, were created by the United States Congress, starting with the Judiciary Act of 1789. For an overview of how the structure and jurisdiction of the federal courts have changed since inception, see United States court reorganization legislation. |
Types of federal courts
- The Supreme Court of the United States is the highest judicial body in the nation and leads the judicial branch of the federal government.
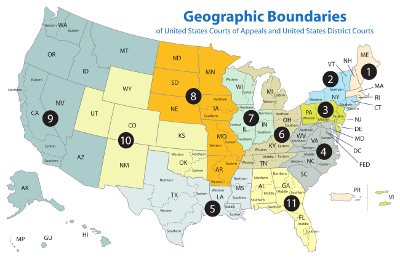
- The United States Courts of Appeals are the intermediate appellate courts of the nation. There are 13 of these courts.
- The United States District Courts are the trial courts of the federal courts. This level of court is composed of 94 different courts.
- The United States Bankruptcy Courts handle matters of bankruptcy across the nation. Courts correspond with the jurisdiction of the United States District Courts.
- There are seven courts of subject-matter jurisdiction in the federal court system. For a summary of these courts, see Federal subject-matter jurisdiction courts.
Federal Circuit Courts by District
This month's Supreme Court arguments
News headlines
- The Federal Judicial Vacancy Count 12/1/2020, Dec 01, 2020
- The Federal Judicial Vacancy Count 11/2/2020, Nov 02, 2020
- The Federal Judicial Vacancy Count 10/1/2020, Oct 02, 2020
- The Federal Judicial Vacancy Count 9/1/2020, Sep 01, 2020





