Union Station: March 8, 2019
Welcome to Union Station, our weekly newsletter that keeps you abreast of the legislation, national trends, and public debate surrounding public-sector union policy. This week, we take a look at two Pennsylvania lawsuits alleging unions collected dues without workers’ consent.
Two lawsuits challenging dues deduction authorizations filed in Pennsylvania
Last week, two lawsuits were filed in U.S. district courts in Pennsylvania alleging unions continued collecting dues from workers without their express consent. (Sources: Pennsylvania Watchdog)
- Who are the parties to the suits?
- Oliver v. SEIU Local 668: The plaintiff is Shalea Oliver, a caseworker for the Pennsylvania Department of Human Services. The primary defendant is SEIU Local 668, the union representing Oliver's collective bargaining unit.
- Adams v. Teamsters Union Local 429: The plaintiffs are Hollie Adams, Jody Weaber, Karen Unger, and Chris Felker, four Lebanon County employees. The primary defendant is Teamsters Union Local 429, the union representing their collective bargaining unit.
- The Liberty Justice Center is representing the plaintiffs in both cases. The Liberty Justice Center also represented the plaintiff in Janus v. AFSCME.
- What is at issue? In both cases, the plaintiffs allege their employers continued to deduct union dues from their paychecks without their express permission. The Liberty Justice Center says any dues deduction authorizations made before the Supreme Court’s Janus decision cannot be enforced.
- What are the parties to the suits saying?
- The Liberty Justice Center said, "Consent cannot be assumed; it must be voluntary, knowing and shown by clear and compelling evidence. Therefore, anything that an employee signed before Janus authorizing union dues be withheld cannot constitute affirmative consent because at the time it was signed the employee was given an unconstitutional choice of paying the union as a member and paying the union as a nonmember."
- We reached out to SEIU Local 668 for comment but had not received a response at press time.
What we're reading
- National Review, "Mark Janus: The Man Who Ended Compulsory Union Dues," March 7, 2019
- The 74, "It’s Been One Year Since the Supreme Court Heard the Janus Case. The Lawsuits Challenging Unions Aren’t Anywhere Near Over," March 5, 2019
- Pennsylvania Business Report, "Sen. Martin introduces bill to eliminate union fair share fees," March 4, 2019
The big picture
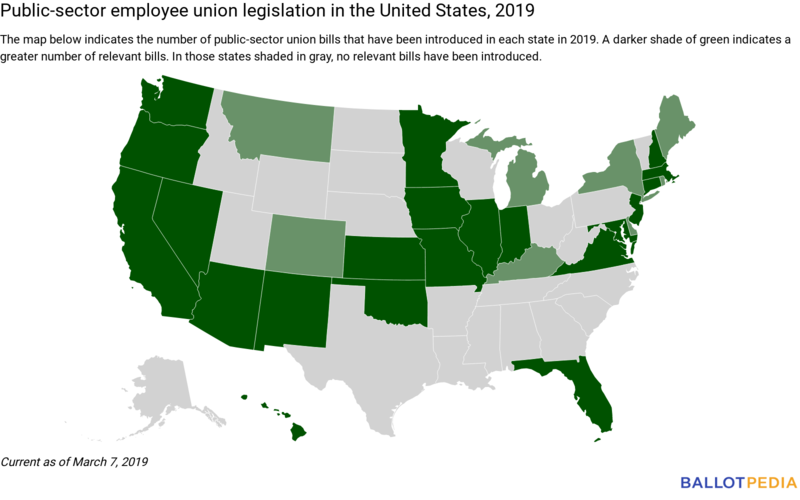
Number of relevant bills by state
We are currently tracking 86 pieces of legislation dealing with public-sector employee union policy. On the map below, a darker shade of green indicates a greater number of relevant bills. Click here for a complete list of all the bills we're tracking.
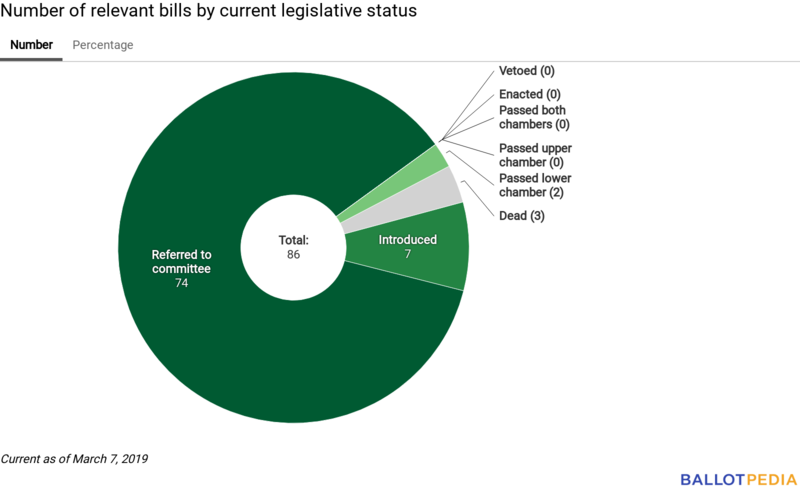
Number of relevant bills by current legislative status
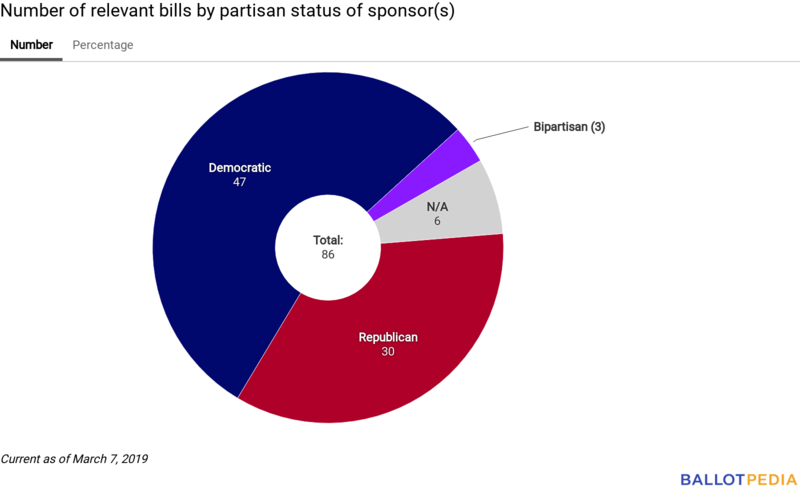
Number of relevant bills by partisan status of sponsor(s)
Recent legislative actions
Below is a complete list of legislative actions on relevant bills since the beginning of the year. Bills are listed in alphabetical order, first by state and then by bill number.
- Connecticut SB00064: This bill would prohibit employers from requiring employees to attend or participate in meetings concerning an employer's views of religious or political matters, including matters related to unions.
- Labor and Public Employees Committee hearing March 5.
- Florida H0013: This bill would prohibit collective bargaining agreements that require public-sector employers to compensate for union activities.
- Oversight, Transparency and Public Management Subcommittee reported favorably March 6.
- Illinois HB2113: This bill would remove language from state statutes requiring public who are not union members to pay agency fees. This bill would also authorize employees to bargain independently with employers.
- Referred to Business and Industry Regulations Subcommittee March 6.
- Illinois HB3455: This bill would exempt unions from requirements to represent non-members. It would also require employers to furnish unions with information on new employees.
- Referred to Labor and Commerce Committee March 5.
- Maryland HB766: This bill would establish collective bargaining rights for community college employees.
- House hearing March 1.
- Maryland HB1143: This bill would establish collective bargaining rights for tenured and tenure-track faculty, graduate students, and adjunct faculty at select public institutions.
- House hearing March 1.
- Maryland SB587: This bill would exempt unions from representing non-members in grievance or contractual proceedings.
- Senate hearing March 7.
- Minnesota HF2072: This bill proposes a constitutional amendment establishing a right to collective bargaining.
- Introduced and referred to Labor Committee March 4.
- New Hampshire SB249: This bill would classify the state Legislature as a public employer under the state's labor laws.
- Finance Committee reported favorably March 5.
- New Mexico HB85: This bill would authorize employers and labor unions to enter into agreements requiring employees to become union members as a condition of employment.
- Senate Judiciary Committee hearing March 6.
- Oregon HB3072: This bill would allow employees to revoke authorizations for dues or fees deductions paid to unions.
- Referred to Business and Labor Committee March 1.
- Oregon HB3244: This bill would prohibit employers from requiring employees to become or remain union members as a condition of employment. It would also prohibit employers from requiring employees to pay fees to unions in lieu of dues as a condition of employment.
- Introduced March 4.
- Washington HB1575: This bill would hold public employers and public-sector unions harmless for claims involving agency fees paid to unions before Janus.
- Placed on second reading March 4.
See also
| |||||||||||||||||||||||