Help us improve in just 2 minutes—share your thoughts in our reader survey.
John Kerry
John Kerry was the special envoy for climate designate for the Biden administration. He resigned from his position in the administration on March 6, 2024.[1][2]
The Biden Transition said of his appointment, "This marks the first time that the [National Security Council] will include an official dedicated to climate change, reflecting the president-elect’s commitment to addressing climate change as an urgent national security issue."[3]
Kerry was the secretary of state under the Obama administration. Kerry was confirmed by the Senate on January 29, 2013, by a vote of 94-3.[4] Kerry previously represented Massachusetts in the Senate from 1985 to 2013. He resigned from the Senate after being nominated by Obama.[4][5]
Biography
Kerry was born in Aurora, Colorado, and his family moved to Massachusetts when he was young. He graduated from Yale University before volunteering for the U.S. Navy and serving two tours of duty in Vietnam. He earned a Silver Star, Bronze Star, and three Purple Hearts.[6] After Kerry unsuccessfully ran for U.S. Congress in 1972, he joined the district attorney's office and earned his J.D. from Boston College.[7] He served as lieutenant governor of Massachusetts under Gov. Michael Dukakis (D) before winning election to the United States Senate in 1984.[8]
Career
Below is an abbreviated outline of Kerry's academic, professional, and political career:[9]
- 2013-2017: U.S. secretary of State
- 2004: Democratic presidential nominee
- 1984-2013: U.S. senator from Massachusetts
- 1982-1984: Lieutenant governor of Massachusetts
- 1977-1982: Assistant district attorney of Massachusetts
- 1976: Graduated from Boston College Law School
- 1972: Ran unsuccessfully for Massachusetts' 5th Congressional District
- 1966-1970: Served in U.S. Navy, including two tours in Vietnam
- 1966: Graduated from Yale
Confirmation vote
Kerry was confirmed as secretary of state on January 29, 2013, by a vote of 94-3. The three votes against Kerry were cast by Ted Cruz (R-Texas), John Cornyn (R-Texas), and Jim Inhofe (R-Okla.). Kerry voted present.[10] Kerry replaced Hillary Clinton as secretary of state.
| John Kerry confirmation vote, January 29, 2013 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Votes for |
Votes against |
Total votes |
| 48 | 0 | 48 | |
| 46 | 3 | 49 | |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Total Votes | 94 | 3 | 97 |
U.S. Senate
Committee assignments
2013
Kerry served on the following Senate committees[11]:
- Foreign Relations Committee Chairman
- Commerce, Science and Transportation Committee
- Finance Committee
- Small Business and Entrepreneurship Committee
2011-2012
During the 112th Congress, Kerry served on the following committees:
- Foreign Relations Committee Chairman
- Small Business and Entrepreneurship Committee
- Finance Committee
- Subcommittee Health Care
- Subcommittee Energy, Natural Resources, and Infrastructure
- Subcommittee Internal Trade, Customs, and Global Competitiveness
- Commerce, Science and Transportation Committee
- Subcommittee Communications, Technology, and the Internet Chairman
- Subcommittee Aviation Operations, Safety, and Security
- Subcommittee Competitiveness, Innovation, and Export Promotion
- Subcommittee Science and Space
- Subcommittee Oceans, Atmosphere, Fisheries, and Coast Guard
- Subcommittee Surface Transportation and Merchant Marine Infrastructure, Safety, and Security
Elections
2008
On November 4, 2008, John Kerry won re-election to the United States Senate. He defeated Jeffrey K. Beatty (R) and Robert J. Underwood (L) in the general election.[12]
2004 presidential election
In 2004, Kerry was defeated by incumbent George W. Bush for the United States presidency.
| U.S. presidential election, 2004 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Candidate | Vote % | Votes | Electoral votes | |
| Republican | 50.8% | 62,039,572 | 286 | ||
| Democratic | John Kerry/John Edwards | 48.3% | 59,027,115 | 251 | |
| Independent | Ralph Nader/Peter Camejo | 0.4% | 465,642 | 0 | |
| Libertarian | Michael Badnarik/Richard Campagna | 0.3% | 397,265 | 0 | |
| Constitution | Michael Peroutka/Charles Baldwin | 0.1% | 144,650 | 0 | |
| Green | David Cobb/Pat LaMarche | 0.1% | 119,910 | 0 | |
| Total Votes | 122,194,154 | 537 | |||
| Election results via: 2004 Presidential General Election Results | |||||
Other candidates that appeared on the ballot received less than 0.1% of the vote. Those candidates included: Leonard Peltier, Walt Brown, Róger Calero, Thomas Harens, Gene Amondson, Bill Van Auken, John Parker, Charles Jay, Stanford Andress and Earl Dodge.[13]
Full history
To view the full congressional electoral history for John Kerry, click [show] to expand the section. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
2002 On November 5, 2002, John Kerry won re-election to the United States Senate. He defeated Michael E. Cloud (L) and Randall Forseberg (Write-in) in the general election.[14] 1996 On November 5, 1996, John Kerry won re-election to the United States Senate. He defeated William F. Weld (R), Susan C. Gallagher (Conservative) and Robert C. Stowe (Natural Law) in the general election.[15] 1990 On November 6, 1990, John Kerry won re-election to the United States Senate. He defeated Jim Rappaport (R) in the general election.[16] 1984 On November 6, 1984, John Kerry won election to the United States Senate. He defeated Raymond Shamie (R) in the general election.[17]
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Campaign donors
2008
Kerry won re-election to the U.S. Senate in 2008. During that re-election cycle, Kerry's campaign committee raised a total of $11,105,663 and spent $17,016,823.[18]
| U.S. Senate, Massachusetts, 2008 - John Kerry Campaign Contributions | |
|---|---|
| Total Raised | $11,105,663 |
| Total Spent | $17,016,823 |
| Total Raised by General Election Opponent | $2,072,027 |
| Total Spent by General Election Opponent | $2,005,358 |
| Top contributors to John Kerry's campaign committee | |
| University of California | $634,225 |
| Harvard University | $365,239 |
| Goldman Sachs | $308,250 |
| Time Warner | $301,624 |
| Citigroup | $296,681 |
| Top 5 industries that contributed to campaign committee | |
| Lawyers/Law Firms | $385,356 |
| Democratic/Liberal | $312,901 |
| Securities & Investment | $243,900 |
| Retired | $187,222 |
| Real Estate | $176,030 |
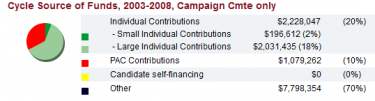
To view the breakdown of campaign funding by type click [show] to expand the section. | |
|---|---|
2002
Kerry won re-election to the U.S. Senate in 2002. During that re-election cycle, Kerry's campaign committee raised a total of $15,468,903 and spent $10,297,909.[19]
His top five contributors between 2003 and 2008 were:
| U.S. Senate election in Massachusetts, 2002 - John Kerry Campaign Contributions | |
|---|---|
| Total Raised | $15,468,903 |
| Total Spent | $10,297,909 |
| Total Raised by General Election Opponent | $182,064 |
| Total Spent by General Election Opponent | $181,984 |
| Top contributors to John Kerry's campaign committee | |
| FleetBoston Financial | $69,000 |
| Interpublic Group | $58,750 |
| Mintz, Levin et al | $54,200 |
| Verizon Communications | $48,206 |
| Raytheon Co | $44,350 |
| Top 5 industries that contributed to campaign committee | |
| Securities & Investment | $11,309 |
| Candidate Committees | $8,500 |
| Finance/Credit Companies | $4,000 |
| Lawyers/Law Firms | $2,600 |
| Electric Utilities | $2,000 |
To view the breakdown of campaign funding by type click [show] to expand the section. | |
|---|---|
Analysis
Ideology and leadership
2012
Based on an analysis of bill sponsorship by GovTrack, Kerry was a "far-left Democratic leader."[20]
National Journal vote ratings
- See also: National Journal vote ratings
National Journal published an analysis of how liberally or conservatively each member of Congress voted, as compared to other members, in the previous year. More information about the analysis process can be found on the vote ratings page.
2012
According to the data released in 2013, Kerry was the 24th most liberal senator during 2012.[21]
2011
According to the data released in 2012, Kerry was the 24th most liberal senator during 2011.[22]
Voting with party
2011
The website OpenCongress tracked how often members of Congress voted with the majority of the chamber caucus. According to the website, Kerry voted with the Democratic Party 95.8 percent of the time, which ranked seventh among the 51 Senate Democrats in November 2012.[23]
Congressional staff salaries
The website Legistorm compiled staff salary information for members of Congress. Kerry paid his congressional staff a total of $2,828,790 in 2011. He ranked 15th on the list of the highest paid Democratic senatorial staff salaries and ranked 20th overall of the highest paid senatorial staff salaries in 2011. Overall, Massachusetts ranked 12th in average salary for senatorial staff. The average U.S. Senate congressional staff was paid $2,529,141.70 in fiscal year 2011.[24]
Net worth
2011
Based on congressional financial disclosure forms and calculations made available by OpenSecrets.org, Kerry's net worth as of 2011 was estimated between $184,268,546 and $287,685,063.00. That averages to $235,976,804.00, which is significantly higher than the average net worth of Democratic senators in 2011 of $20,795,449.53. His average calculated net worth[25] increased by 1.84 percent from 2010.[26]
2010
Based on congressional financial disclosure forms and calculations made available by OpenSecrets.org, Kerry's net worth as of 2010 was estimated between $181,469,521 and $281,976,067. That averages to $231,722,794, which is higher than the average net worth of Democratic senators in 2010 of $19,383,524 .[27]
Notable endorsements
This section displays endorsements this individual made in elections within Ballotpedia's coverage scope.
Personal
Note: Please contact us if the personal information below requires an update.
Kerry is married to Theresa Heinz. He and his first wife, Julia Thorne, divorced in 1988. Kerry has two children from his first marriage, Alexandra and Vanessa. He also has three stepsons, H. John Heinz IV, Andre Heinz, and Christopher Heinz.
Recent news
This section links to a Google news search for the term John + Kerry + Secretary + State
See also
- Joe Biden presidential transition
- U.S. Department of State
- Massachusetts
- United States Senate
- Massachusetts Lieutenant Governor
- Crisis in Gaza, 2014
- ISIS insurgency in Iraq and Syria
- George W. Bush
- Hillary Clinton
External links
Footnotes
- ↑ The Washington Post, "A veteran adviser is taking over as top U.S. climate diplomat," January 31, 2024
- ↑ Fox Baltimore, "John Kerry to resign from Biden admin climate role Wednesday," March 4, 2024
- ↑ Biden-Harris Transition, "President-Elect Biden Announces Key Members of Foreign Policy and National Security Team," November 23, 2020
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 The Washington Post, "John Kerry confirmed as secretary of state," January 29, 2013
- ↑ CBS News, "Obama taps John Kerry to be Secretary of State," December 21, 2012
- ↑ Biography.com, "John Kerry," accessed September 17, 2013
- ↑ Boston College, "Secretary of State John Kerry to Boston College Class of 2014: 'Pass On Your Light to Others,'" May 19, 2014
- ↑ Biography.com, "John Kerry biography," accessed September 3, 2014
- ↑ Biographical Directory of the United States Congress, "John Forbes Kerry," accessed August 27, 2011
- ↑ Politico, "Senate backs Max Baucus for China ambassador," February 6, 2014
- ↑ Congressional Quarterly, "Senate Committee List," accessed January 22, 2013
- ↑ U.S. Congress House Clerk, "Statistics of the Congressional Election of November 4, 2008," accessed March 28, 2013
- ↑ U.S. Election Atlas, "2004 Presidential General Election," accessed September 18, 2013
- ↑ U.S. Congress House Clerk, "Statistics of the Congressional Election of November 5, 2002," accessed March 28, 2013
- ↑ U.S. Congress House Clerk, "Statistics of the Congressional Election of November 5, 1996," accessed March 28, 2013
- ↑ U.S. Congress House Clerk, "Statistics of the Congressional Election of November 6, 1990," accessed March 28, 2013
- ↑ U.S. Congress House Clerk, "Statistics of the Congressional Election of November 6, 1984," accessed March 28, 2013
- ↑ OpenSecrets, "John Kerry 2008 Election Cycle," accessed October 2011
- ↑ OpenSecrets, "John Kerry 2002 Election Cycle," accessed October 2011
- ↑ GovTrack, "John Kerry," accessed March 3, 2012
- ↑ National Journal, "TABLE: House Liberal Scores by Issue Area," February 26, 2013
- ↑ National Journal, "Searchable Vote Ratings Tables: House," accessed February 23, 2012
- ↑ OpenCongress, "Voting With Party," archived November 7, 2012
- ↑ LegiStorm, "John Kerry," accessed September 3, 2014
- ↑ This figure represents the total percentage growth from either 2004 (if the member entered office in 2004 or earlier) or the member's first year in office (as noted in the chart below).
- ↑ OpenSecrets, "Kerry, (D-Massachusetts), 2011," accessed September 3, 2014
- ↑ OpenSecrets, "Kerry, (D-Massachusetts), 2010," accessed September 3, 2014
| Political offices | ||
|---|---|---|
| Preceded by Hillary Clinton |
U.S. Secretary of State 2013-2017 |
Succeeded by - |
| Preceded by Paul Tsongas |
U.S. Senate - Massachusetts 1985-2013 |
Succeeded by Mo Cowan |
State of Massachusetts Boston (capital) | |
|---|---|
| Elections |
What's on my ballot? | Elections in 2025 | How to vote | How to run for office | Ballot measures |
| Government |
Who represents me? | U.S. President | U.S. Congress | Federal courts | State executives | State legislature | State and local courts | Counties | Cities | School districts | Public policy |