San Joaquin Basin
This article does not receive scheduled updates. If you would like to help our coverage grow, consider donating to Ballotpedia. Contact our team to suggest an update.
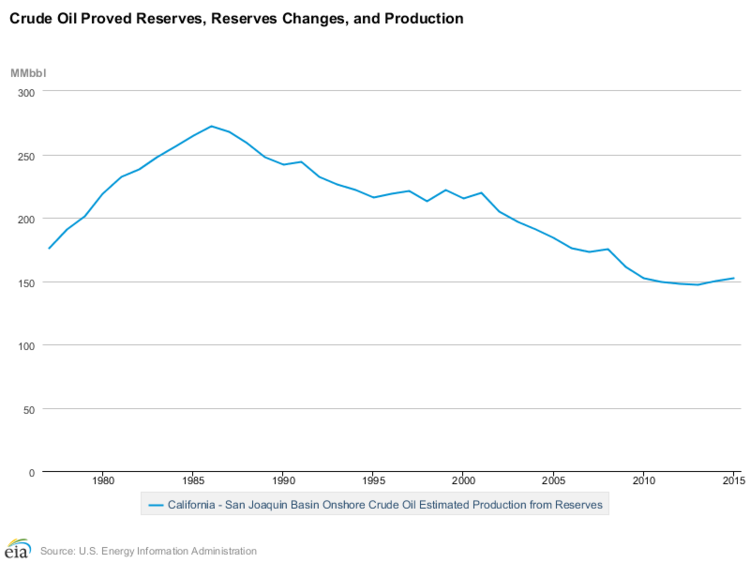
The San Joaquin Basin is located in western-central California and contains petroleum production. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), crude oil production in the basin totaled approximately 152 million barrels in 2015, which accounted for 75.5 percent of total crude oil production in California.[1]
Background
The San Joaquin Basin is located in western-central California and spans portions of Fresno, Kern, Kings, Merced, Madera, Monterey, San Luis Obispo, San Joaquin, Stanislaus and Tulare counties.[1]
Oil and natural gas production in the San Joaquin Basin began in the late 19th century. Large-scale oil production using wooden derricks began in the basin in 1878. The discovery of the Kern River oil field in 1899 led to increased oil production in the San Joaquin Basin. In 1903, California became the top petroleum-producing state.[2]
Beginning in the 1960s, oil and gas operators nationwide began using thermal recovery technology, which involves injecting steam into an oil field to heat thicker forms of crude oil to ease the extraction process. This technology was subsequently adopted by operators in the San Joaquin Basin. In 1986, crude oil production at the Kern River oil field in the basin totaled 47.8 million barrels.[2][3]
In 2003, the U.S. Geological Survey assessed potential petroleum and natural gas deposits in the region and found five petroleum systems (the geological processes and elements needed to generate, accumulate, and store petroleum, natural gas, and other hydrocarbons). The survey concluded that the basin contained up to 393 million barrels of crude oil, 1.8 trillion cubic feet of natural gas]], and 86 million barrels of natural gas liquids in the five petroleum systems. As of 2012, the basin contained three of the 10 largest oil fields in the United States in terms of total production and proved reserves.[1]
Production
In 2015, crude oil production in the San Joaquin Basin totaled 152 million barrels—75.5 percent of total California crude oil production. The chart below shows crude oil production in the basin from 1977 to 2015 (in million barrels of oil).[4]
See also
Footnotes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 U.S. Geological Survey, "Petroleum Systems and Geological Assessment of Oil and Gas in the San Joaquin Basin Province, California," January 29, 2013
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Kenneth I. Takahashi and Donald L. Gautier with the U.S. Geological Survey, "A Brief History of Oil and Gas Exploration in the Southern San Joaquin Valley of California," accessed April 24, 2014
- ↑ U.S. Geological Survey, "Assessment of Remaining Recoverable Oil in Selected Major Oil Fields of the San Joaquin Basin, California," accessed April 25, 2017
- ↑ U.S. Energy Information Administration, "California San Joaquin Basin Onshore - Crude Oil Proved Reserves, Reserve Changes, and Production," accessed April 24, 2017