Historical Illinois budget and finance information
![]() This article does not contain the most recently published data on this subject. If you would like to help our coverage grow, consider donating to Ballotpedia.
This article does not contain the most recently published data on this subject. If you would like to help our coverage grow, consider donating to Ballotpedia.
The historical Illinois budget and finance information below applies to years prior to the most current fiscal year. With the exception of the tab labeled "Prior fiscal year budgets," the tabs below display information, from several different fiscal years, as it was presented on Ballotpedia in prior calendar years. For more current information regarding Illinois' budget and finances, click here.
As published 2016
| Illinois budget and finances | |
| General information | |
| Budget calendar: Annual | |
| Fiscal year: 2017 | |
| State credit rating: A- (as of 2014) | |
| Current governor: Bruce Rauner | |
| Financial figures | |
| Total spending (state and federal funds): $69.4 billion (estimated for 2015) | |
| Per capita spending: $5,397.36 (estimated for 2015) | |
| Total state tax collections: $39.2 billion (2014) | |
| Per capita tax collections: $3,041.63 (2014) | |
| State debt: $321.4 billion (as of 2014) | |
| Per capita state debt: $24,959 (as of 2014) | |
| State budget and finance pages • Total state expenditures • State debt • Tax policy in Illinois | |
In Illinois, as in other states, lawmakers and public officials are elected in part to manage the state's finances. This includes generating revenues (money coming into the state from various sources) and approving expenditures (the money spent on governmental functions and servicing state debt). State budgets are complex and fluid, as they depend on anticipated revenues and planned expenditures, which may alter over the course of a fiscal year. If revenues do not keep pace with expenditures, states generally have to raise taxes, cut services, borrow money, or a combination of the three. State budget decisions are also influenced by policy decisions at the national level, such as the Affordable Care Act or energy and environmental regulations, and issues at the local level, such as crime and the quality of education.
The Illinois state budget and financial data presented here come from different years because the states and the federal government report and publish the information at different times.
Definitions
The following terms are used to describe a state's finances:
- Revenues come mainly from tax collections, licensing fees, federal aid, and returns on investments.
- Expenditures generally include spending on government salaries, infrastructure, education, public pensions, public assistance, corrections, Medicaid, and transportation.
- State debt refers to the money borrowed to make up for a deficit when revenues do not cover spending.
- The state credit rating is the grade given by a credit rating agency based on the general financial health of the state's government and economy.
- State funds include general and other state-based funds. A general fund is "the predominant fund for financing a state's operations." Other state funds are "restricted by law for particular governmental functions or activities."[4]
- Federal funds are "funds received directly from the federal government."[4]
- Total spending is calculated by adding together the totals for state and federal funds used for expenditures.
Revenues
2014 revenues
The table below breaks down state government tax collections by source in 2014 (comparable figures from surrounding states are also provided to give additional context). Figures for all columns except "2013 population" and "Per capita collections" are rendered in thousands of dollars (for example, $2,448 translates to $2,448,000). Figures in the columns labeled "2013 population" and "Per capita collections" have not been abbreviated.[5]
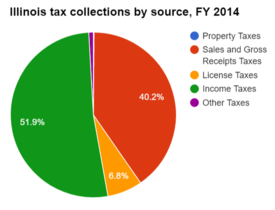
Compared to neighboring states, Illinois had the highest state tax collections per capita, at $3,042.
| State tax collections by source ($ in thousands), 2014 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | Property taxes | Sales and gross receipts | Licenses | Income taxes | Other taxes | Total | 2013 population | Per capita collections |
| Illinois | $54,710 | $15,758,509 | $2,675,943 | $20,343,042 | $350,690 | $39,182,894 | 12,882,189 | $3,042 |
| Indiana | $8,052 | $10,395,150 | $590,483 | $5,763,064 | $90,212 | $16,846,961 | 6,597,880 | $2,553 |
| Michigan | $1,919,910 | $12,309,564 | $1,511,695 | $8,755,723 | $307,081 | $24,803,973 | 9,916,306 | $2,501 |
| Ohio | N/A | $15,617,920 | $2,928,276 | $8,424,843 | $49,586 | $27,020,625 | 11,596,998 | $2,330 |
| Wisconsin | $159,069 | $7,359,539 | $1,040,619 | $7,779,733 | $71,965 | $16,410,925 | 5,759,432 | $2,849 |
| United States | $14,232,835 | $411,414,175 | $51,120,024 | $357,104,785 | $31,880,270 | $865,752,089 | 318,907,401 | $2,715 |
| Source: U.S. Census Bureau, "2014 annual survey of state government tax collections by category," accessed April 4, 2016 | ||||||||
The table below lists 2014 tax collections by source as percentages of total collections. About 51.9 percent of Illinois' total state tax collections came from income taxes.[5]
| State tax collections by source (as percentages), 2014 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | Property taxes | Sales and gross receipts | Licenses | Income taxes | Other taxes |
| Illinois | 0.1% | 40.2% | 6.8% | 51.9% | 0.9% |
| Indiana | 0.0% | 61.7% | 3.5% | 34.2% | 0.5% |
| Michigan | 7.7% | 49.6% | 6.1% | 35.3% | 1.2% |
| Ohio | N/A | 57.8% | 10.8% | 31.2% | 0.2% |
| Wisconsin | 1.0% | 44.8% | 6.3% | 47.4% | 0.4% |
| Source: U.S. Census Bureau, "2014 annual survey of state government tax collections by category," accessed April 4, 2016 | |||||
Federal aid to the state budget
- See also: Federal aid to state budgets
State governments receive aid from the federal government to fund a variety of joint programs, mainly in the form of grants for such things as Medicaid, education, and transportation. In 2013 federal aid to the states accounted for roughly 30 percent of all state general revenues. Federal aid varies from state to state. For example, Mississippi received approximately $7.5 billion in federal aid in 2013, accounting for about 43 percent of the state's general revenues, the highest percentage of all of the states. By contrast, North Dakota received about $1.5 billion in federal aid in 2013, or just 19 percent of the state's general revenues, the lowest percentage in the nation.[6]
The table below notes what share of Illinois’ general revenues came from the federal government in 2013. That year, Illinois received approximately $17 billion in federal aid, 25.9 percent of the state's general revenues. Taking into consideration the state's 2013 population, this came out to about $1,318 in federal aid per capita. Figures from surrounding states are provided for additional context.[7]
| Federal aid to state budgets, 2013 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | Total federal aid ($ in thousands) | Federal aid as a % of general revenues | Ranking (by % of general revenues) | Est. 2013 population | Aid per capita |
| Illinois | $16,973,577 | 25.9% | 40 | 12,882,135 | $1,318 |
| Indiana | $11,192,452 | 33.4% | 20 | 6,570,902 | $1,703 |
| Michigan | $17,829,882 | 32.8% | 23 | 9,895,622 | $1,802 |
| Ohio | $20,482,575 | 33.6% | 19 | 11,570,808 | $1,770 |
| Wisconsin | $8,952,020 | 27.7% | 36 | 5,742,713 | $1,559 |
| Sources: United States Census Bureau, "State Government Finances: 2013," accessed April 4, 2016 United States Census Bureau, "State totals: Vintage 2013," accessed April 8, 2016 Note: Per-capita figures were generated by Ballotpedia by dividing total federal aid for the state by the estimated population of that state in 2013. | |||||
Spending
Estimated 2015 expenditures
- See also: Total state expenditures
The table below breaks down estimated spending totals for fiscal year 2015 (comparable figures from surrounding states are included to provide additional context). Figures for all columns except "Population” and “Per capita spending" are rendered in millions of dollars (for example, $2,448 translates to $2,448,000,000). Figures in the columns labeled "Population” and “Per capita spending" have not been abbreviated.[2]
Illinois' total estimated government spending in fiscal year 2015 was $69.4 billion, which was the highest amount when compared to surrounding states.
| Total estimated state spending, FY 2015 ($ in millions) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | State funds | Federal funds | Total spending | Population | Per capita spending |
| Illinois | $51,506 | $17,904 | $69,410 | 12,859,995 | $5,397.36 |
| Indiana | $19,037 | $10,305 | $29,342 | 6,619,680 | $4,432.54 |
| Michigan | $31,232 | $22,633 | $53,865 | 9,922,576 | $5,428.53 |
| Ohio | $48,593 | $13,994 | $62,587 | 11,613,423 | $5,389.19 |
| Wisconsin | $34,275 | $11,122 | $45,397 | 5,771,337 | $7,865.94 |
| Per-capita figures are calculated by taking the state's total spending and dividing by the number of state residents according to United States Census Bureau estimates.[8] Source: National Association of State Budget Officers, "Examining fiscal 2013-2015 state spending," accessed April 4, 2016 | |||||
Spending by function
State spending in Illinois can be further broken down by function (elementary and secondary education, public assistance, etc.). Fiscal year 2014 information is included in the table below (information from neighboring states is provided for additional context). Figures are rendered as percentages, indicating the share of the total budget spent per category.[2]
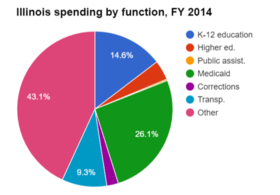
In fiscal year 2014, Medicaid accounted for 26.1 percent of Illinois' total expenditures.
| State spending by function as a percent of total expenditures, FY 2014 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | K-12 education | Higher education | Public assistance | Medicaid | Corrections | Transportation | Other |
| Illinois | 14.6% | 4.1% | 0.3% | 26.1% | 2.4% | 9.3% | 43.1% |
| Indiana | 32.0% | 6.6% | 1.5% | 32.0% | 2.8% | 5.9% | 19.2% |
| Michigan | 26.9% | 4.3% | 0.5% | 27.6% | 4.4% | 7.5% | 28.7% |
| Ohio | 16.8% | 4.2% | 1.3% | 35.8% | 3.0% | 6.3% | 32.5% |
| Wisconsin | 16.1% | 14.2% | 0.4% | 18.4% | 2.8% | 6.6% | 41.5% |
| Source: National Association of State Budget Officers Note: "Other" expenditures include "Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP), institutional and community care for the mentally ill and developmentally disabled, public health programs, employer contributions to pensions and health benefits, economic development, environmental projects, state police, parks and recreation, housing and general aid to local governments."[2] | |||||||
Spending trends
Between 2010 and 2014, the share of the Illinois state budget spent on K-12 education from 18.2 percent in 2010 to 14.6 percent in 2014. See the table below for further details (figures are rendered as percentages, indicating the share of the total budget spent per category).[2][9][10]
| Spending by function from 2010 to 2014 (as percentages) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | K-12 education | Higher education | Public assistance | Medicaid | Corrections | Transportation | Other |
| 2014 | 14.6% | 4.1% | 0.3% | 26.1% | 2.4% | 9.3% | 43.1% |
| 2013 | 13.3% | 3.7% | 0.3% | 23.8% | 2.1% | 8.4% | 48.4% |
| 2012 | 15.8% | 5.5% | 0.1% | 19.7% | 2.2% | 8.5% | 48.1% |
| 2011 | 18.9% | 5.6% | 1.0% | 32.9% | 2.9% | 11.4% | 27.4% |
| 2010 | 18.2% | 4.5% | 0.2% | 23.6% | 2.0% | 8.1% | 43.3% |
| Source: National Association of State Budget Officers Note: "Other" expenditures include "Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP), institutional and community care for the mentally ill and developmentally disabled, public health programs, employer contributions to pensions and health benefits, economic development, environmental projects, state police, parks and recreation, housing and general aid to local governments."[2] | |||||||
Fiscal year budgets
Fiscal year 2016
Governor Bruce Rauner proposed his fiscal year 2016 budget in February 2015. In June, the Republican governor signed a fiscal year 2016 education budget, but the state's general budget had not yet been passed as of December 18, 2015.[11][12]
The governor's budget proposed cuts in spending while recommending reforms in state pension and other budgets. The governor also prioritized paying off debts while also building up the state's rainy day fund.[13]
State debt
- See also: State debt
According to a January 2014 report by the nonprofit organization State Budget Solutions, Illinois had a state debt of approximately $321.4 billion. Its state debt per capita was $24,959, fifth highest in the country. In this report for fiscal year 2012, state debt was based on four components: "market-valued unfunded public pension liabilities, outstanding government debt, unfunded other post employment benefit (OPEB) liabilities, and outstanding unemployment trust fund loans." The report revealed that all state governments faced a combined $5.1 trillion in debt, which amounted to an obligation of $16,178 per capita in the nation.[14]
| Total 2012 state debt | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| State | Total state debt | State debt per capita | Per capita debt ranking |
| Illinois | $321,354,115,000 | $24,959 | 5 |
| Indiana | $46,377,635,000 | $7,094 | 48 |
| Michigan | $142,668,026,000 | $14,435 | 25 |
| Ohio | $321,340,764,000 | $27,836 | 4 |
| Wisconsin | $45,026,643,000 | $7,863 | 47 |
| Sources: State Budget Solutions, "State Budget Solutions' Fourth Annual State Debt Report," January 8, 2014 | |||
Taxpayer burden
|
TIA Methodology: To figure a state’s taxpayer burden or surplus, TIA looked at a state’s total reported assets minus capital assets and assets restricted by law (buildings, roads, land, etc.) to calculate “available assets,” which were then compared to the amount of money the state owes in bills, including retirement obligations such as pension plans and healthcare benefits for retirees. If the difference between available assets and total bills was positive, TIA called this a surplus; if it was negative, this was a burden. This amount was then divided by the number of individual tax returns with a positive tax liability, thus expressing the total state surplus or burden on a per-taxpayer basis. |
According to a report released in September 2015 by the nonprofit Truth in Accounting (TIA), Illinois ranked 3rd worst in the country in “taxpayer burden.” Rather than using per capita state debt, TIA ranked states based on what it called a “taxpayer burden,” a term that reflects “the amount each taxpayer would have to send to their state’s treasury in order for the state to be debt-free.” On the other hand, states that had sufficient resources to pay their bills were said to have a “taxpayer surplus,” which represents the amount that each taxpayer would receive if the state were to disburse its excess funds.
Based on analysis of Illinois’ Comprehensive Annual Financial Report from June 30, 2014 and actuarial reports for the state’s retirement plans, TIA concluded that $157.5 billion in promised retirement benefits were unfunded, but only $39.8 billion of these liabilities were reported on Illinois’ balance sheet. With all of the unfunded retirement benefits included in the total debt, the state had a shortfall of $184.3 billion, or a taxpayer burden of $45,000.[15]
Public pensions
- See also: Illinois public pensions and Illinois public employee salaries
Between fiscal years 2008 and 2012, the funded ratio of Illinois' state-administered pension plans decreased from 54.3 percent to 40.4 percent. The state paid 76 percent of its annual required contribution, and for fiscal year 2012 the pension system's unfunded accrued liability totaled $94.5 billion. This amounted to $7,421 in unfunded liabilities per capita.[16][17]
Credit ratings
- See also: State credit ratings
Credit rating agencies, such as Standard and Poor's, assign grades to states that take into account a state's ability to pay debts and the general health of the state's economy. Generally speaking, a higher credit rating indicates lower interest costs on the general obligation bonds states sometimes sell to investors in order to finance large-scale undertakings (e.g., road construction and other public works projects). This in turn results in lower interest costs, thereby lowering the cost to taxpayers.[18][19]
The table below lists the Standard and Poor's credit ratings for Illinois and surrounding states from 2004 to 2014. Standard and Poor's grades range from AAA, the highest available, to BBB, the lowest.[20]
| State credit ratings, 2004 to 2014 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | 2005 | 2004 |
| Illinois | A- | A- | A | A+ | A+ | A+ | AA | AA | AA | AA | AA |
| Indiana | AAA | AAA | AAA | AAA | AAA | AAA | AAA | AA+ | AA+ | AA | AA |
| Michigan | AA- | AA- | AA- | AA- | AA- | AA- | AA- | AA- | AA | AA | AA+ |
| Ohio | AA+ | AA+ | AA+ | AA+ | AA+ | AA+ | AA+ | AA+ | AA+ | AA+ | AA+ |
| Wisconsin | AA | AA | AA | AA | AA | AA | AA | AA- | AA- | AA- | AA- |
| Source: Stateline: The Daily News Service of The Pew Charitable Trusts, "Infographic: S&P State Credit Ratings, 2001-2014," June 9, 2014 | |||||||||||
Economic indicators
- See also: Economic indicators by state
Broadly defined, a healthy economy is typically one that has a "stable and strong rate of economic growth" (gross state product, in this case) and low unemployment, among many other factors. The economic health of a state can significantly affect its healthcare costs, insurance coverage, access to care, and citizens' physical and mental health. For instance, during economic downturns, employers may reduce insurance coverage for employees, while those who are laid off may lose coverage altogether. Individuals also tend to spend less on non-urgent care or postpone visits to the doctor when times are hard. These changes in turn may affect the decisions made by policymakers as they react to shifts in the industry. Additionally, a person's socioeconomic status has profound effects on their access to care and the quality of care received.[21][22][23]
In September 2014, Illinois had an unemployment rate of 6.6 percent, higher than any of its neighboring states. Most residents in Illinois earned incomes at least 400 percent above the federal poverty level, with a median annual household income of $54,083.[24][25][26][27]
Note: Gross state product (GSP) on its own is not necessarily an indicator of economic health; GSP may also be influenced by state population size. Many factors must be looked at together to assess state economic health.
| Various economic indicators by state | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | Distribution of population by FPL* (2013) | Median annual income (2011-2013) | Unemployment rate | Total GSP (2013)† | ||||
| Under 100% | 100-199% | 200-399% | 400%+ | Sept. 2013 | Sept. 2014 | |||
| Illinois | 13% | 17% | 31% | 39% | $54,083 | 9.1% | 6.6% | $720,692 |
| Indiana | 12% | 23% | 31% | 35% | $48,178 | 7.3% | 5.7% | $317,102 |
| Iowa | 11% | 18% | 35% | 36% | $53,364 | 4.5% | 4.6% | $165,767 |
| Wisconsin | 11% | 15% | 31% | 42% | $54,205 | 6.6% | 5.5% | $282,486 |
| United States | 15% | 19% | 30% | 36% | $52,047 | 7.2% | 5.9% | $16,701,415 |
| * Federal Poverty Level. "The U.S. Census Bureau's poverty threshold for a family with two adults and one child was $18,751 in 2013. This is the official measurement of poverty used by the Federal Government." † Median annual household income, 2011-2013. ‡ In millions of current dollars. "Gross State Product is a measurement of a state's output; it is the sum of value added from all industries in the state." Source: The Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation, "State Health Facts" | ||||||||
Budget process
Illinois operates on an annual budget cycle. The sequence of key events in the budget process is:[28][29]
- In September and October of the year preceding the start of the new fiscal year, the governor sends budget instructions to state agencies.
- In October and November, agencies submit their budget requests to the governor.
- Budget hearings with the public are held from February through May.
- On the third Wednesday in February, the governor submits his or her proposed budget to the Illinois General Assembly.
- The General Assembly passes a budget in May.
Illinois is one of 44 states in which the governor has line item veto authority.[29][30]
The governor is constitutionally required to submit a balanced budget. In turn, the legislature must pass a balanced budget.[29]
Agencies, offices and committees
The following standing committees in the Illinois General Assembly deal with budget and finance matters:
- Appropriations I Committee, Illinois State Senate
- Appropriations II Committee, Illinois State Senate
- Appropriations-Elementary & Secondary Education Committee, Illinois House of Representatives
- Appropriations-General Service Committee, Illinois House of Representatives
- Appropriations-Higher Education Committee, Illinois House of Representatives
- Appropriations-Human Services Committee, Illinois House of Representatives
- Appropriations-Public Safety Committee, Illinois House of Representatives
- Revenue & Finance Committee, Illinois House of Representatives
The Illinois Treasurer is the state's chief financial officer and is responsible for overseeing the state's funds, managing investments and disbursing monies. The treasurer is elected every four years and is a partisan position.
The Illinois Comptroller maintains the state's fiscal accounts and oversees withdrawals from and deposits into the state's accounts. The comptroller is elected every four years and is a partisan position.
Transparency
- See also: "Following the Money" report, 2015
The U.S. Public Interest Research Group, a consumer-focused nonprofit organization based in Washington, D.C., released its annual report on state transparency websites in March 2015. The report, entitled "Following the Money," measured how transparent and accountable state websites were with regard to state government spending.[31] According to the report, Illinois received a grade of A- and a numerical score of 93, indicating that Illinois was "Leading" in terms of transparency regarding state spending.[31]
As published 2015
|
The information on this tab contains:
|
Between fiscal years 2013 and 2014, total spending in Illinois increased by approximately $4 billion, from $66.4 billion in fiscal year 2013 to an estimated $70.4 billion in 2014. This represents a 5.9 percent increase. The cumulative rate of inflation during the same period was 1.58 percent, calculated using the Consumer Price Indices for January 2013 and January 2014. As of 2014, financial services firm Standard and Poor's had assigned Illinois a credit rating of A-.[32][33][34]
Spending
Definitions
The following terms are used to describe a state's finances:
- Revenues come mainly from tax collections, licensing fees, federal aid, and returns on investments.
- Expenditures generally include spending on government salaries, infrastructure, education, public pensions, public assistance, corrections, Medicaid, and transportation.
- State debt refers to the money borrowed to make up for a deficit when revenues do not cover spending.
- The state credit rating is the grade given by a credit rating agency based on the general financial health of the state's government and economy.
- State funds include general and other state-based funds. A general fund is "the predominant fund for financing a state's operations." Other state funds are "restricted by law for particular governmental functions or activities."[4]
- Federal funds are "funds received directly from the federal government."[4]
- Total spending is calculated by adding together the totals for state and federal funds used for expenditures.
2014 expenditures
- See also: Total state expenditures
The table below breaks down estimated spending totals for fiscal year 2014 (comparable figures from surrounding states are included to provide additional context). Figures for all columns except "Population” and “Per capita spending" are rendered in millions of dollars (for example, $2,448 translates to $2,448,000,000). Figures in the columns labeled "Population” and “Per capita spending" have not been abbreviated.[34]
Total estimated spending in Illinois amounted to $70.4 billion, highest among its neighboring states. Estimated per capita spending was second-highest among neighboring states at $5,462.
| Total estimated state spending, FY 2014 ($ in millions) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | State funds | Federal funds | Total spending | Population | Per capita spending |
| Illinois | $50,392 | $19,964 | $70,356 | 12,880,580 | $5,462.18 |
| Indiana | $17,282 | $9,978 | $27,260 | 6,596,855 | $4,132.27 |
| Michigan | $30,605 | $20,632 | $51,237 | 9,909,877 | $5,170.30 |
| Ohio | $46,043 | $13,046 | $59,089 | 11,594,163 | $5,096.44 |
| Wisconsin | $33,887 | $11,006 | $44,893 | 5,757,564 | $7,797.22 |
| Per-capita figures are calculated by taking the state's total spending and dividing by the number of state residents according to United States Census Bureau estimates.[35] Source: National Association of State Budget Officers | |||||
Spending by function
State spending in Illinois can be further broken down by function (elementary and secondary education, public assistance, etc.). Fiscal year 2013 information is included in the table below (information from neighboring states is provided for additional context). Figures are rendered as percentages, indicating the share of the total budget spent per category.[34]
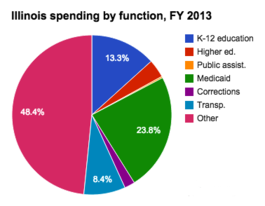
In 2013 Illinois dedicated 23.8 percent of its budget to Medicaid, the largest single portion. The bulk of its budget was dedicated to expenditures labeled as "Other." The share dedicated to K-12 education was lower than its neighbors at 13.3 percent.
| State spending by function as a percent of total expenditures, FY 2013 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | K-12 education | Higher education | Public assistance | Medicaid | Corrections | Trans- portation |
Other |
| Illinois | 13.3% | 3.7% | 0.3% | 23.8% | 2.1% | 8.4% | 48.4% |
| Indiana | 30.8% | 6.1% | 1.4% | 31.2% | 2.7% | 8.3% | 19.6% |
| Michigan | 27.2% | 4.2% | 0.7% | 26.4% | 4.6% | 7.8% | 29% |
| Ohio | 17% | 4.3% | 1.5% | 29.2% | 3.2% | 5.1% | 39.8% |
| Wisconsin | 16.2% | 14.3% | 0.3% | 17.2% | 2.9% | 6.9% | 42.1% |
| Source: National Association of State Budget Officers Note: "Other" expenditures include "Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP), institutional and community care for the mentally ill and developmentally disabled, public health programs, employer contributions to pensions and health benefits, economic development, environmental projects, state police, parks and recreation, housing and general aid to local governments."[34] | |||||||
Spending trends
Between 2009 and 2013, the portion of the budget Illinois dedicated to K-12 education decreased by about 10 percentage points, from 23.9 percent to 13.3 percent. The share dedicated to Medicaid also decreased from 30.9 percent to 23.8 percent. Meanwhile, the portion spent on expenditures labeled as "Other" increased from 26.6 percent to 48.4 percent. See the table below for further details (figures are rendered as percentages, indicating the share of the total budget spent per category).[34][9][10][36][37]
| Spending by function from 2009 to 2013 (as percentages) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | K-12 education | Higher education | Public assistance | Medicaid | Corrections | Transportation | Other |
| 2013 | 13.3% | 3.7% | 0.3% | 23.8% | 2.1% | 8.4% | 48.4% |
| 2012 | 15.8% | 5.5% | 0.1% | 19.7% | 2.2% | 8.5% | 48.1% |
| 2011 | 18.9% | 5.6% | 1.0% | 32.9% | 2.9% | 11.4% | 27.4% |
| 2010 | 18.2% | 4.5% | 0.2% | 23.6% | 2.0% | 8.1% | 43.3% |
| 2009 | 23.9% | 6.3% | 0.3% | 30.9% | 3.0% | 9.0% | 26.6% |
| Source: National Association of State Budget Officers Note: "Other" expenditures include "Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP), institutional and community care for the mentally ill and developmentally disabled, public health programs, employer contributions to pensions and health benefits, economic development, environmental projects, state police, parks and recreation, housing and general aid to local governments."[34] | |||||||
Revenues
2013 revenues
The table below breaks down state government tax collections by source in 2013 (comparable figures from surrounding states are also provided to give additional context). Figures for all columns except "Population" and "Per capita revenue" are rendered in thousands of dollars (for example, $2,448 translates to $2,448,000). Figures in the columns labeled "Population" and "Per capita revenue" have not been abbreviated.[5]
Total tax collections in Illinois amounted to $38.7 billion, while per capita collections came out to $3,003. Both figures were highest among neighboring states.
| State tax collections by source ($ in thousands) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | Property taxes | Sales and gross receipts | Licenses | Individual income taxes | Corporation net income taxes | Other taxes | Total | 2013 population | Per capita collections |
| Illinois | $61,806 | $14,705,739 | $2,583,108 | $16,538,662 | $4,462,627 | $363,378 | $38,715,320 | 12,890,552 | $3,003.39 |
| Indiana | $7,008 | $10,298,491 | $699,373 | $4,976,375 | $781,585 | $167,899 | $16,930,731 | 6,570,713 | $2,576.70 |
| Michigan | $1,954,898 | $12,268,026 | $1,454,634 | $8,239,086 | $900,667 | $265,343 | $25,082,654 | 9,898,193 | $2,534.06 |
| Ohio | N/A | $13,636,046 | $3,445,620 | $9,869,545 | $262,226 | $117,511 | $27,330,948 | 11,572,005 | $2,361.82 |
| Wisconsin | $148,600 | $7,088,411 | $1,035,743 | $7,227,690 | $955,752 | $66,416 | $16,522,612 | 5,742,953 | $2,877.02 |
| Source: Tax Policy Center, "State Tax Collection Sources 2000-2013," June 20, 2014 | |||||||||
The table below lists 2013 tax collections by source as percentages of total collections. In Illinois, individual income taxes accounted for the bulk of total collections at 42.7 percent.[5]
| State tax collections by source (as percentages) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | Property taxes | Sales and gross receipts | Licenses | Individual income taxes | Corporation net income taxes | Other taxes |
| Illinois | 0.16% | 37.98% | 6.67% | 42.72% | 11.53% | 0.94% |
| Indiana | 0.04% | 60.83% | 4.13% | 29.39% | 4.62% | 0.99% |
| Michigan | 7.79% | 48.91% | 5.8% | 32.85% | 3.59% | 1.06% |
| Ohio | N/A | 49.89% | 12.61% | 36.11% | 0.96% | 0.43% |
| Wisconsin | 0.9% | 42.9% | 6.27% | 43.74% | 5.78% | 0.4% |
| Source: Tax Policy Center, "State Tax Collection Sources 2000-2013," June 20, 2014 | ||||||
State debt
- See also: State debt
According to a January 2014 report by the nonprofit organization State Budget Solutions, Illinois had a state debt of approximately $321.4 billion. Its state debt per capita was $24,959, fifth highest in the country. In this report for fiscal year 2012, state debt was based on four components: "market-valued unfunded public pension liabilities, outstanding government debt, unfunded other post employment benefit (OPEB) liabilities, and outstanding unemployment trust fund loans." The report revealed that all state governments faced a combined $5.1 trillion in debt, which amounted to an obligation of $16,178 per capita in the nation.[38]
| Total 2012 state debt | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| State | Total state debt | State debt per capita | Per capita debt ranking |
| Illinois | $321,354,115,000 | $24,959 | 5 |
| Indiana | $46,377,635,000 | $7,094 | 48 |
| Michigan | $142,668,026,000 | $14,435 | 25 |
| Ohio | $321,340,764,000 | $27,836 | 4 |
| Wisconsin | $45,026,643,000 | $7,863 | 47 |
| Sources: State Budget Solutions, "State Budget Solutions' Fourth Annual State Debt Report," January 8, 2014 | |||
Taxpayer burden
According to a report released in September 2015 by the nonprofit Truth in Accounting (TIA), Illinois ranked 3rd worst in the country in “taxpayer burden.” Rather than using per capita state debt, TIA ranked states based on what it called a “taxpayer burden,” a term that reflects “the amount each taxpayer would have to send to their state’s treasury in order for the state to be debt-free.” On the other hand, states that had sufficient resources to pay their bills were said to have a “taxpayer surplus,” which represents the amount that each taxpayer would receive if the state were to disburse its excess funds.[15]
To figure a state’s taxpayer burden/surplus, TIA looks at a state’s total reported assets minus capital assets and assets restricted by law (buildings, roads, land, etc.) to calculate “available assets.” TIA then compares available assets to the amount of money the state owes in bills, which includes retirement obligations such as pension plans and health care benefits for retirees. If the difference between available assets and total bills is positive, TIA calls this a surplus; if it’s negative, this is called a burden. TIA then divides this amount by the number of taxpayers in the state (specifically, the number of individual tax returns with a positive tax liability), thus expressing the total state surplus or burden on a per-taxpayer basis.
Based on analysis of Illinois’ Comprehensive Annual Financial Report from June 30, 2014 and actuarial reports for the state’s retirement plans, TIA concluded that $157.5 billion in promised retirement benefits were unfunded, but only $39.8 billion of these liabilities were reported on Illinois’ balance sheet. With all of the unfunded retirement benefits included in the total debt, the state had a shortfall of $184.3 billion, or a taxpayer burden of $45,000.[15]
Public pensions
- See also: Illinois public pensions and Illinois public employee salaries
Between fiscal years 2008 and 2012, the funded ratio of Illinois' state-administered pension plans decreased from 54.3 percent to 40.4 percent. The state paid 76 percent of its annual required contribution, and for fiscal year 2012 the pension system's unfunded accrued liability totaled $94.5 billion. This amounted to $7,421 in unfunded liabilities per capita.[16][39]
Credit ratings
- See also: State credit ratings
Credit rating agencies, such as Standard and Poor's, assign grades to states that take into account a state's ability to pay debts and the general health of the state's economy. Generally speaking, a higher credit rating indicates lower interest costs on the general obligation bonds states sometimes sell to investors in order to finance large-scale undertakings (e.g., road construction and other public works projects). This in turn results in lower interest costs, thereby lowering the cost to taxpayers.[18][40]
The table below lists the Standard and Poor's credit ratings for Illinois and surrounding states from 2004 to 2014. Standard and Poor's grades range from AAA, the highest available, to BBB, the lowest.[41]
| State credit ratings, 2004 to 2014 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | 2005 | 2004 |
| Illinois | A- | A- | A | A+ | A+ | A+ | AA | AA | AA | AA | AA |
| Indiana | AAA | AAA | AAA | AAA | AAA | AAA | AAA | AA+ | AA+ | AA | AA |
| Michigan | AA- | AA- | AA- | AA- | AA- | AA- | AA- | AA- | AA | AA | AA+ |
| Ohio | AA+ | AA+ | AA+ | AA+ | AA+ | AA+ | AA+ | AA+ | AA+ | AA+ | AA+ |
| Wisconsin | AA | AA | AA | AA | AA | AA | AA | AA- | AA- | AA- | AA- |
| Source: Stateline: The Daily News Service of The Pew Charitable Trusts, "Infographic: S&P State Credit Ratings, 2001-2014," June 9, 2014 | |||||||||||
Federal aid to the state budget
- See also: Federal aid to state budgets
State governments receive aid from the federal government to fund a variety of joint programs, such as Medicaid. Federal aid varies from state to state. For example, Mississippi received approximately $7.7 billion in federal aid in 2012, which accounted for more than 45 percent of the state's general revenues. By contrast, Alaska received roughly $2.9 billion in federal aid in 2012, just under 20 percent of the state's general revenues.[7]
The table below notes what share of Illinois’ general revenues came from the federal government in 2012. That year, Illinois received approximately $15.6 in federal aid, 25.7 percent of the state's total general revenues. Figures from surrounding states are provided for additional context.[7]
| Federal aid to state budgets, 2012 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| State | Total federal aid ($ in thousands) | Federal aid as a % of general revenue | Ranking |
| Illinois | $15,646,844 | 25.66% | 43 |
| Indiana | $10,441,125 | 32.32% | 29 |
| Michigan | $17,849,942 | 33.76% | 24 |
| Ohio | $20,687,909 | 34.88% | 17 |
| Wisconsin | $8,855,079 | 28.19% | 38 |
| Source: United States Census Bureau, "State Government Finances: 2012," accessed February 24, 2014 | |||
Stimulus
According to Recovery.gov, the official government website for the Recovery Accountability and Transparency Board, under the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act, Illinois received $9.1 billion in federal stimulus funding between February 2009 and June 2013.[42]
Budget process
Illinois operates on an annual budget cycle. The sequence of key events in the budget process is:[43][29]
- In September and October of the year preceding the start of the new fiscal year, the governor sends budget instructions to state agencies.
- In October and November, agencies submit their budget requests to the governor.
- Budget hearings with the public are held from February through May.
- On the third Wednesday in February, the governor submits his or her proposed budget to the Illinois General Assembly.
- The General Assembly passes a budget in May.
Illinois is one of 44 states in which the governor has line item veto authority.[29][44]
The governor is constitutionally required to submit a balanced budget. In turn, the legislature must pass a balanced budget.[29]
Agencies, offices, and committees
The following standing committees in the Illinois General Assembly deal with budget and finance matters:
- Appropriations I Committee, Illinois State Senate
- Appropriations II Committee, Illinois State Senate
- Appropriations-Elementary & Secondary Education Committee, Illinois House of Representatives
- Appropriations-General Service Committee, Illinois House of Representatives
- Appropriations-Higher Education Committee, Illinois House of Representatives
- Appropriations-Human Services Committee, Illinois House of Representatives
- Appropriations-Public Safety Committee, Illinois House of Representatives
- Revenue & Finance Committee, Illinois House of Representatives
The Illinois Treasurer is the state's chief financial officer and is responsible for overseeing the state's funds, managing investments and disbursing monies. The treasurer is elected every four years and is a partisan position.
The Illinois Comptroller maintains the state's fiscal accounts and oversees withdrawals from and deposits into the state's accounts. The comptroller is elected every four years and is a partisan position.
Studies and reports
U.S. PIRG "Following the Money" report
- See also: "Following the Money" report, 2014
The U.S. Public Interest Research Group, a consumer-focused nonprofit organization based in Washington, D.C., released its annual report on state transparency websites in April 2014. The report, entitled "Following the Money," measured the transparency and accountability of state websites with regard to state government spending.[45] According to the report, Illinois received a grade of B+ and a numerical score of 88, indicating that Illinois was advancing in terms of transparency regarding state spending.[45]
As published 2014
|
The information on this tab contains:
|
Between fiscal year 2009 and fiscal year 2013, total expenditures in Illinois increased by approximately $17.1 billion, from $49.3 billion in 2009 to $66.4 billion in 2013. This represented a 25.6 percent increase, outpacing the cumulative rate of inflation during the same period (9.06 percent, calculated using the Consumer Price Indices for January 2009 and January 2013).[46][47]
Spending
Definitions
Although each state executes its budget process differently, the National Association of State Budget Officers (NASBO) breaks down state expenditures into four general categories. This allows for comparisons among the 50 states. NASBO's categories are as follows:[48]
- General fund: "The predominant fund for financing a state’s operations. Revenues are received from broad-based state taxes. However, there are differences in how specific functions are financed from state to state."[48]
- Other funds: "Expenditures from revenue sources that are restricted by law for particular governmental functions or activities. For example, a gasoline tax dedicated to a highway trust fund would appear in the 'Other funds' column. For Medicaid, other state funds include provider taxes, fees, donations, assessments, and local funds."[48]
- Federal funds: "Funds received directly from the federal government."[48]
- Bonds: "Expenditures from the sale of bonds, generally for capital projects."[48]
2013
2013 expenditures
The table below breaks down expenditures for fiscal year 2013 (comparable figures from surrounding states are provided to give additional context).[48] Figures for all columns except "Per capita expenditures" are rendered in millions of dollars (for example, $2,448 translates to $2,448,000,000). Figures in the column labeled "Per capita expenditures" have not been abbreviated.
| Total state expenditures, FY 2013 ($ in millions)[48] | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
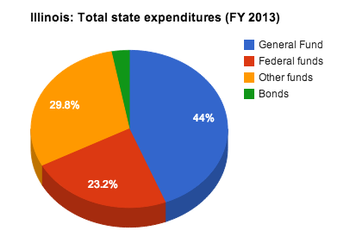
| State | General fund | Federal funds | Other funds | Bonds | Total | Per capita expenditures** | |
| Illinois | $29,260 | $15,407 | $19,825 | $1,955 | $66,447 | $5,158.07 | |
| Indiana | $14,189 | $10,357 | $3,220 | $0 | $27,766 | $4,225.60 | |
| Michigan | $9,164 | $19,295 | $20,107 | $182 | $48,748 | $4,926.22 | |
| Ohio | $31,514 | $12,630 | $12,950 | $1,174 | $58,268 | $5,035.78 | |
| Wisconsin | $14,042 | $10,815 | $17,912 | $0 | $42,769 | $7,447.53 | |
| **Per capita figures are calculated by taking the state's total expenditures and dividing by the number of state residents according to United States Census estimates.[49] Source: National Association of State Budget Officers | |||||||
Spending by function
2012
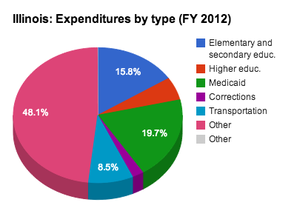
Source: National Association of State Budget Officers
State expenditures in Illinois can be further broken down by function (elementary and secondary education, public assistance, etc.). Fiscal year 2012 data is included in the table below (information from neighboring states is provided for additional context). Figures are rendered as percentages, indicating the share of the total budget spent per category.
| Expenditures by function, FY 2012 (as percentages)[48] | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | Elementary and secondary ed. | Higher ed. | Public assistance | Medicaid | Corrections | Transportation | Other |
| Illinois | 15.8% | 5.5% | 0.1% | 19.7% | 2.2% | 8.5% | 48.1% |
| Indiana | 32.9% | 6.5% | 1.5% | 27.3% | 2.9% | 9.3% | 19.7% |
| Michigan | 27.2% | 4.1% | 0.9% | 26.1% | 4.7% | 6.9% | 30.2% |
| Ohio | 20.6% | 4.2% | 1.5% | 24.4% | 3.1% | 5.1% | 41.2% |
| Wisconsin | 16.7% | 14.1% | 0.4% | 16.5% | 2.9% | 6.9% | 42.5% |
| Source: National Association of State Budget Officers Note: "Other" expenditures include "Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP), institutional and community care for the mentally ill and developmentally disabled, public health programs, employer contributions to pensions and health benefits, economic development, environmental projects, state police, parks and recreation, housing and general aid to local governments."[48] | |||||||
Spending trends
From 2008 to 2012, expenditures for education, public assistance, Medicaid and corrections decreased. During the same time period, expenditures for transportation increased by 0.2 percentage points, a 2.4 percent increase in the share of the budget, and expenditures for other budget items increased by 16.9 percentage points, a 54.2 percent increase in the share of the budget. The table below details changes in expenditures from 2008 to 2012.[48][9][10][36][37]
Figures are rendered as percentages, indicating the share of the total budget spent per category.
| Expenditures from 2008 to 2012 (as percentages) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Elementary and secondary ed. | Higher ed. | Public assistance | Medicaid | Corrections | Transportation | Other |
| 2012 | 15.8% | 5.5% | 0.1% | 19.7% | 2.2% | 8.5% | 48.1% |
| 2011 | 18.9% | 5.6% | 1.0% | 32.9% | 2.9% | 11.4% | 27.4% |
| 2010 | 18.2% | 4.5% | 0.2% | 23.6% | 2.0% | 8.1% | 43.3% |
| 2009 | 23.9% | 6.3% | 0.3% | 30.9% | 3.0% | 9.0% | 26.6% |
| 2008 | 21.8% | 6.0% | 0.3% | 29.5% | 3.0% | 8.3% | 31.2% |
| Change in % | -6.0% | -0.5% | -0.2% | -9.8% | -0.8% | 0.2% | 16.9% |
| Source: National Association of State Budget Officers Note: "Other" expenditures include "Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP), institutional and community care for the mentally ill and developmentally disabled, public health programs, employer contributions to pensions and health benefits, economic development, environmental projects, state police, parks and recreation, housing and general aid to local governments."[48] | |||||||
Revenues
2013 revenues
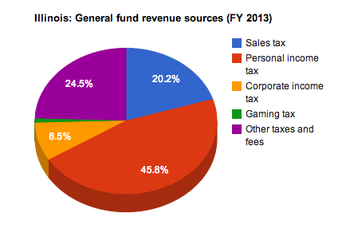
Source: National Association of State Budget Officers
The table below breaks down general fund revenues by source in fiscal year 2013 (comparable figures from surrounding states are also provided to give additional context).[48] Figures for all columns except "Per capita revenue" are rendered in millions of dollars (for example, $2,448 translates to $2,448,000,000). Figures in the column labeled "Per capita revenue" have not been abbreviated.
| Revenue sources in the general fund, FY 2013 ($ in millions)[48] | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | Sales tax | Personal income tax | Corporate income tax | Gaming tax | Other taxes and fees | Total | Per capita revenue |
| Illinois | $7,335 | $16,630 | $3,086 | $340 | $8,899 | $36,290 | $2,817.08 |
| Indiana | $6,796 | $4,978 | $968 | $555 | $1,165 | $14,462 | $2,200.92 |
| Michigan | $1,832 | $5,844 | $438 | $0 | $1,075 | $9,189 | $928.59 |
| Ohio | $8,445 | $9,508 | $262 | $0 | $11,344 | $29,559 | $2,554.62 |
| Wisconsin | $4,410 | $7,497 | $925 | $0 | $1,254 | $14,086 | $2,554.62 |
| **Per capita figures are calculated by taking the state's total revenues and dividing by the number of state residents according to United States Census estimates for 2013.[49] Source: National Association of State Budget Officers | |||||||
Revenue trends
The table below details the change in revenue sources in the general fund from 2009 to 2013.[48][9] Figures for all columns except "Per capita revenue" are rendered in millions of dollars (for example, $2,448 translates to $2,448,000,000). Figures in the column labeled "Per capita revenue" have not been abbreviated.
| Revenue sources in the general fund, Illinois ($ in millions)[48][9] | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Sales tax | Personal income tax | Corporate income tax | Gaming tax | Other taxes and fees | Total | Per capita revenue |
| 2013 | $7,335 | $16,630 | $3,086 | $340 | $8,899 | $36,290 | $2,817.08 |
| 2012 | $7,226 | $15,512 | $2,461 | $340 | $8,083 | $33,622 | $2,612.80 |
| 2011 | $6,833 | $11,225 | $1,851 | $324 | $9,930 | $30,163 | $2,346.23 |
| 2010 | $6,308 | $8,510 | $1,360 | $383 | $4,884 | $21,445 | $1,670.21 |
| 2009 | $6,772 | $9,223 | $1,710 | $430 | $4,441 | $22,577 | $1,748.74 |
| Change in % | 8.31% | 80.31% | 80.47% | -20.93% | 100.38% | 60.74% | 61.09% |
| **Per capita figures are calculated by taking the state's total revenues and dividing by the number of state residents according to United States Census estimates.[49][50] Source: National Association of State Budget Officers | |||||||
Historical spending
The information on state budget historical spending below was compiled by the National Association of State Budget Officers. Figures reflect the reported "Total Expenditures" in Table 1. Figures for all columns are rendered in millions of dollars (for example, $2,448 translates to $2,448,000,000).[48][10]
| Historical state spending in Illinois ($ in millions) | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fiscal year | General Fund | Other funds | Federal funds | Bonds | Budget totals | ||||||||||||
| Total | % of Budget | Total | % of Budget | Total | % of Budget | Total | % of Budget | ||||||||||
| 2011-2012 | $29,257 | 45% | $14,944 | 23% | $19,407 | 30% | $2,122 | 3% | $65,730 | ||||||||
| 2010-2011 | $25,237 | 45% | $14,375 | 25% | $14,821 | 26% | $1,957 | 3% | $56,390 | ||||||||
| 2009-2010 | $26,316 | 53% | $10,021 | 20% | $12,083 | 25% | $895 | 2% | $49,315 | ||||||||
| Averages: | $26,937 | 47% | $13,113 | 23% | $15,437 | 27% | $1,658 | 3% | $57,145 | ||||||||
Budget transparency
| Transparency evaluation | ||
|---|---|---|
| Illinois Open Book | Illinois Transparency and Accountability | |
| Searchability | ||
| Grants | ||
| Contracts | ||
| Line item expenditures | ||
| Dept./agency budgets | ||
| Public employee salaries | ||
| Last evaluated in 2009. | ||
Article 4, Section 8 of the Illinois Constitution requires three "title" reads on three separate days. It also requires that a bill must be printed in its entirety and placed on the desk of members before final passage. There is no provision for a length time between when the bill is placed on the desk and when a vote may be taken.[51]
Government tools
The table to the right is helpful in evaluating the transparency of the Illinois Open Book and Illinois Accountability and Transparency websites.
In March 2009, Governor Pat Quinn launched "Budget Illinois," which summarized the proposed budget for 2010, offered budget figures and also detailed a capital projects list, including information on the recommended and actual appropriations and expenditures going forward.[52][53]
State budget websites and analysis
Until 2011, the Illinois Office of Management and Budget website did not post copies of the budget proposals from previous fiscal years. This was unusual, given that many other states' budget offices keep archived copies of past budgets. For the 2011 budget, the state adopted a more transparent method of publishing its budget, providing the information on a quarterly and annual basis. The new process did not affect how agency budgets would be audited. These reports were to be released for a year or more after revenue and costs were available.[54]
Limitations and Suggestions
- Add a copy of the actual contracts to Open Book.
- Provide line-item spending information on the Comptroller's aggregate expenditure information website.
Multi-measure budget transparency profile
The Institute of Government and Public Affairs at the University of Illinois created a multi-measure transparency profile for Illinois, which measured state transparency as of September 2011 using indicators from a range of organizations. These indicators measured both website transparency and other recognized facets of governmental transparency. In addition, IGPA presented four unique indicators of non-transparency based on the observation that transfers or reassignments between general and special funds can obscure the true fiscal condition of a state.[55][56]
IGPA devised a budget transparency index based on information available from the National Association of State Budget Officers. Illinois tied for 33rd in the nation with 12 other states, earning four out of eight possible points.[56]
| Illinois - IGPA score for budget process, contents and disclosure | |
|---|---|
| Budget transparency indicator | Yes or no? |
| Performance measures | |
| "Generally Accepted Accounting Principles" budget | |
| Multi-year forecasting | |
| Annual cycle | |
| Binding revenue forecast | |
| Legislative revenue forecast | |
| Nonpartisan staff | |
| Constitution or statutory tax/spend limitations | |
| TOTAL | 4 |
In addition to the individual state profile, IGPA offered a 50-state comparison and profiles for other states.[56]
U.S. PIRG "Following the Money" report
- See also: "Following the Money" report, 2014
The U.S. Public Interest Research Group, a consumer-focused nonprofit organization based in Washington, D.C., released its annual report on state transparency websites in April 2014. The report, entitled "Following the Money," measured how transparent and accountable state websites were with regard to state government spending.[45] According to the report, Illinois received a grade of B+ and a numerical score of 88, indicating that Illinois was an "advancing" state in terms of transparency regarding state spending.[45]
Prior fiscal year budgets
Fiscal year 2016
Governor Bruce Rauner proposed his fiscal year 2016 budget in February 2015. In June, the Republican governor signed a fiscal year 2016 education budget, but the state's general budget was not passed as of March 31, 2016.[57][58]
The governor's budget proposed cuts in spending while recommending reforms in state pension and other budgets. The governor also prioritized paying off debts while also building up the state's rainy day fund.[13]
Fiscal year 2015
![]() See budget bill: Fiscal Year 2015 Budget
See budget bill: Fiscal Year 2015 Budget
Governor Pat Quinn announced his fiscal year 2015 budget proposal on March 26, 2014. Under the governor's proposal, the operating budget for fiscal year 2015 would have equaled approximately $65.9 billion, including $32.2 billion in general fund expenditures. For all funds, this represents a 2.4 percent increase over fiscal year 2014.[2]
On June 30, 2014, Quinn signed into law the fiscal year 2015 budget. The enacted operating budget totaled $66.4 billion, including $31.5 billion in general fund spending. Quinn vetoed approximately $250 million for state capitol renovations.[2][59]
Fiscal year 2014
![]() See budget bill: House Bill 215
See budget bill: House Bill 215
| Illinois state budget -- 2014 | |
| Illinois State Legislature | |
| Text: | HB 215 |
| Legislative history | |
| Introduced: | January 25, 2013 |
| House: | May 28, 2013 |
| Vote (lower house): | 69-47 |
| Senate: | May 31, 2013 |
| Vote (upper house): | 38-20 |
| Governor: | Pat Quinn |
| Signed: | July 2, 2013 |
| Vetoed: | Line Item and Reduction Vetoes |
The fiscal year 2014 budget was signed into law by Governor Pat Quinn on July 2, 2013, after using line item and reduction vetoes.[60] The enacted budget reduced the backlog of unpaid bills to $5.8 billion, but pension costs totaled $7.65 billion, representing 24.3 percent of General Funds revenues. According to the Institute for Illinois' Fiscal Sustainability, such pension costs represented an unsustainable level and were expected to rise in coming years without reform.[61]
Fiscal year 2013
- See also: Illinois state budget (2012-2013)
Fiscal year 2012
- See also: Illinois state budget (2011-2012)
Fiscal year 2011
- See also: Illinois state budget (2010-2011)
Fiscal year 2010
- See also: Illinois state budget (2009-2010)
See also
Footnotes
- ↑ Bureau of Labor Statistics, "CPI Detailed Report Data for February 2015," accessed April 4, 2016
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 National Association of State Budget Officers, "Examining fiscal 2013-2015 state spending," accessed April 4, 2016 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "nasbo2015" defined multiple times with different content Cite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name "nasbo2015" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ InflationData.com, "Cumulative Inflation Calculator," accessed April 4, 2016. The cumulative rate of inflation during the same period declined -0.1 percent, calculated using the Consumer Price Indices for January 2014 and January 2015.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 National Association of State Budget Officers, "State Expenditure Report: 2013-2015," accessed April 7, 2016
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 U.S. Census Bureau, "2014 annual survey of state government tax collections by category," accessed April 4, 2016 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "taxcollections" defined multiple times with different content Cite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name "taxcollections" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ United States Census Bureau, "State Government Finances: 2013," accessed March 21, 2016
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 United States Census Bureau, "State Government Finances: 2012," accessed February 24, 2014
- ↑ United States Census Bureau, "State and County QuickFacts," accessed April 4, 2016
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 National Association of State Budget Officers, "State Expenditure Report, 2009-2011," accessed February 24, 2014
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 National Association of State Budget Officers, "State Expenditures Report, 2010-2012," accessed February 24, 2014
- ↑ Reuters.com, "Illinois governor signs first fiscal year 2016 budget bill," accessed September 24, 2015
- ↑ Fox 32 Chicago, "Illinois leaders report minor progress in state budget talks," accessed December 18, 2015
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 National Association of State Budget Officers, "Summaries of Fiscal Year 2016 Proposed and Enacted Budgets," accessed September 22, 2015
- ↑ State Budget Solutions, "State Budget Solutions' Fourth Annual State Debt Report," January 8, 2014
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 Truth in Accounting, "Financial State of the States," September 2015 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "tia" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ 16.0 16.1 Morningstar, "The State of State Pension Plans 2013: A Deep Dive Into Shortfalls and Surpluses," accessed September 16, 2013
- ↑ The Pew Charitable Trusts, “The Fiscal Health of State Pension Plans: Funding Gap Continues to Grow,” accessed April 16, 2015
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 Stateline: The Daily News Service of The Pew Charitable Trusts, "Infographic: S&P State Credit Ratings, 2001-2012," July 13, 2012
- ↑ Bankrate, "The 6 states with the worst credit ratings," September 27, 2012
- ↑ Stateline: The Daily News Service of The Pew Charitable Trusts, "Infographic: S&P State Credit Ratings, 2001-2014," June 9, 2014
- ↑ Academy Health, "Impact of the Economy on Health Care," August 2009
- ↑ The Conversation, "Budget explainer: What do key economic indicators tell us about the state of the economy?" May 6, 2015
- ↑ Health Affairs, "Socioeconomic Disparities In Health: Pathways And Policies," accessed July 13, 2015
- ↑ The Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation, "Distribution of Total Population by Federal Poverty Level," accessed July 17, 2015
- ↑ The Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation, "Median Annual Household Income," accessed July 17, 2015
- ↑ The Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation, "Unemployment Rate (Seasonally Adjusted)," accessed July 17, 2015
- ↑ The Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation, "Total Gross State Product (GSP) (millions of current dollars)," accessed July 17, 2015
- ↑ National Conference of State Legislatures, "State Experiences with Annual and Biennial Budgeting," accessed February 4, 2021
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 29.2 29.3 29.4 29.5 National Association of State Budget Officers, "Budget Processes in the States, Spring 2021," accessed January 24, 2023
- ↑ National Conference of State Legislatures, "Separation of Powers: Executive Veto Powers," accessed January 26, 2024
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 U.S. Public Interest Research Group, "Following the Money 2015 Report," accessed April 4, 2016
- ↑ Bureau of Labor Statistics, "CPI Detailed Report Data for February 2014," accessed April 9, 2014
- ↑ InflationData.com, "Cumulative Inflation Calculator," February 28, 2014
- ↑ 34.0 34.1 34.2 34.3 34.4 34.5 National Association of State Budget Officers, "State Expenditure Report: 2012-2014," accessed February 18, 2015
- ↑ United States Census Bureau, "State and County QuickFacts," accessed February 23, 2014
- ↑ 36.0 36.1 National Association of State Budget Officers, "State Expenditure Report, 2009," accessed February 24, 2014
- ↑ 37.0 37.1 National Association of State Budget Officers, "State Expenditure Report, 2008," accessed February 24, 2014
- ↑ State Budget Solutions, "State Budget Solutions' Fourth Annual State Debt Report," January 8, 2014
- ↑ The Pew Charitable Trusts, “The Fiscal Health of State Pension Plans: Funding Gap Continues to Grow,” accessed April 16, 2015
- ↑ Bankrate, "The 6 states with the worst credit ratings," September 27, 2012
- ↑ Stateline: The Daily News Service of The Pew Charitable Trusts, "Infographic: S&P State Credit Ratings, 2001-2014," June 9, 2014
- ↑ Recovery, "Stimulus Spending by State," accessed March 19, 2015
- ↑ National Conference of State Legislatures, "State Experiences with Annual and Biennial Budgeting," accessed February 4, 2021
- ↑ National Conference of State Legislatures, "Separation of Powers: Executive Veto Powers," accessed January 26, 2024
- ↑ 45.0 45.1 45.2 45.3 U.S. Public Interest Research Group, "Following the Money 2014 Report," accessed April 15, 2014
- ↑ Bureau of Labor Statistics, "CPI Detailed Report Data for February 2014," accessed April 9, 2014
- ↑ InflationData.com, "Cumulative Inflation Calculator," February 28, 2014
- ↑ 48.00 48.01 48.02 48.03 48.04 48.05 48.06 48.07 48.08 48.09 48.10 48.11 48.12 48.13 48.14 48.15 National Association of State Budget Officers, "State Expenditure Report, 2011-2013," accessed February 21, 2014
- ↑ 49.0 49.1 49.2 United States Census Bureau, "Annual Estimates of the Resident Population: April 1, 2010 to July 1, 2013," accessed February 26, 2014
- ↑ United States Census Bureau, "Vintage 2009: Annual Population Estimates," accessed February 26, 2014
- ↑ Illinois Constitution, "Article 4, Section 8," accessed 2009
- ↑ Budget Illinois
- ↑ State of Illinois - Budget, March 19, 2009
- ↑ Chicago Press Release, "Governor’s Office of Management and Budget Improves Transparency by Releasing Quarterly Financial Reports – Financial Statements Now Available Without Delay," Dec. 9, 2010
- ↑ Institute of Government and Public Affairs at University of Illinois, "Home page," accessed February 21, 2014
- ↑ 56.0 56.1 56.2 Institute of Government and Public Affairs at University of Illinois, "Budget Transparency Profiles - All 50 States," September 2011
- ↑ Reuters.com, "Illinois governor signs first fiscal year 2016 budget bill," accessed September 24, 2015
- ↑ Fox 32 Chicago, "Illinois leaders report minor progress in state budget talks," accessed December 18, 2015
- ↑ Illinois Office of Management and Budget, "Budget Books - Fiscal Year 2015 - Table I-A - Operating and Capital," accessed September 23, 2014
- ↑ Illinois General Assembly, "Bill Status of HB0215," accessed April 22, 2014
- ↑ Institute for Illinois' Fiscal Sustainability, "State of Illinois Enacted FY2014 Budget: A Review of the Operating and Capital Budgets for the Current Fiscal Year," October 2, 2013
State of Illinois Springfield (capital) | |
|---|---|
| Elections |
What's on my ballot? | Elections in 2026 | How to vote | How to run for office | Ballot measures |
| Government |
Who represents me? | U.S. President | U.S. Congress | Federal courts | State executives | State legislature | State and local courts | Counties | Cities | School districts | Public policy |