It’s the 12 Days of Ballotpedia! Your gift powers the trusted, unbiased information voters need heading into 2026. Donate now!
Auditor (state executive office): Difference between revisions
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 233: | Line 233: | ||
==Election history== | ==Election history== | ||
===2026=== | |||
::''See also: [[State executive official elections, 2026]]'' | |||
'''Fourteen states''' {{Greener|start=11/3/2026 9:00pm CDT|before=are holding|after=held}} elections for auditor in 2026: | |||
{{colbegin|2}} | |||
* [[Alabama Auditor election, 2026|Alabama]] | |||
* [[Arkansas Auditor election, 2026|Arkansas]] | |||
* [[Delaware Auditor election, 2026|Delaware]] | |||
* [[Iowa Auditor election, 2026|Iowa]] | |||
* [[Massachusetts Auditor election, 2026|Massachusetts]] | |||
* [[Minnesota Auditor election, 2026|Minnesota]] | |||
* [[Missouri Auditor election, 2026|Missouri]] | |||
* [[Nebraska Auditor election, 2026|Nebraska]] | |||
* [[New Mexico Auditor election, 2026|New Mexico]] | |||
* [[Ohio Auditor election, 2026|Ohio]] | |||
* [[Oklahoma Auditor election, 2026|Oklahoma]] | |||
* [[South Dakota Auditor election, 2026|South Dakota]] | |||
* [[Vermont Auditor election, 2026|Vermont]] | |||
* [[Wyoming Auditor election, 2026|Wyoming]] | |||
{{colend}} | |||
===2025=== | ===2025=== | ||
::''See also: [[State executive official elections, 2025]]'' | ::''See also: [[State executive official elections, 2025]]'' | ||
| Line 385: | Line 406: | ||
*[[State Auditor reports]] | *[[State Auditor reports]] | ||
*[[Comprehensive Annual Financial Report]] (CAFR) | *[[Comprehensive Annual Financial Report]] (CAFR) | ||
* [[State executive official elections, 2024]] | * [[State executive official elections, 2024]] | ||
* [[State executive official elections, 2025]] | |||
* [[State executive official elections, 2026]] | |||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
Latest revision as of 17:13, 8 December 2025
| State Executive Offices |
| Elections by Year |
| 2025 • 2024 • 2023 • 2022 • 2021 • 2020 • 2019 • 2018 • 2017 • 2016 • 2015 • 2014 • 2013 • 2012 • 2011 |
| State Executive Analyses |
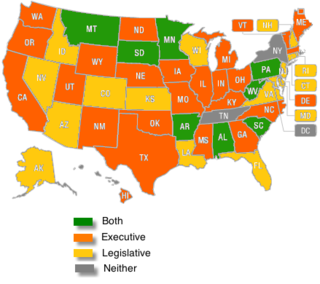
The auditor is a state-level position in 48 states that supervises and has administrative rights over the accounting and financial functions of the state. Additionally, auditors act as watchdogs over other state agencies, performing internal government audits, and investigating fraud allegations.
The state auditor belongs to either the executive or legislative branch, depending on the state. While both offices are similar in function, a legislative auditor functions primarily under the state legislature and is not considered a state executive office.
The auditor may be elected or appointed, depending on the state. Terms of office range from four to 10 years and may be indefinite, served at the pleasure of the appointing body. In instances where the auditor is an appointee, appointment is usually done through some form of nomination in a subcommittee of the legislature and a confirmatory vote before the General Assembly.
Some states assign the same portfolio to another state level financial officer, such as the treasurer or the comptroller.
There are a total of 23 legislative auditor offices and 33 state executive auditor offices. A total of eight states have both auditor offices.
Current officeholders
Among appointed auditors, it is common for a dedicated legislative committee to nominate an auditor, who is then confirmed by a simple majority vote of both legislative chambers. Many appointed auditors serve at the pleasure of the legislature or a specific committee charged with audits. In these states, an auditor may be removed with either a simple majority or a three-fifths vote at any time.
Appointed auditors serve as nonpartisan officials, with the exception of Connecticut, where Democrats and Republicans each have one nomination, resulting in two partisan auditors who share the office.
In each of the 24 states where the auditor is elected, it is a partisan position.
Elected auditors are overwhelmingly Constitutional offices, with 20 of 24 states providing for the office in the state's Constitution.
List of current state executive auditors
Comparison across states
While most states that do have a statewide governmental auditor position authorize the governor to appoint an individual to the office, there are at least 24 others who have opted to have public voters select these officeholders. These states include: Alabama, Arkansas, Delaware, Indiana, Iowa, Kentucky, Massachusetts, Minnesota, Missouri, Mississippi, Montana, Nebraska, New Mexico, North Carolina, North Dakota, Ohio, Oklahoma, Pennsylvania, South Dakota, Utah, Vermont, Washington, West Virginia and Wyoming.
Two states - New York and Tennessee - do not have an official auditor. Audit functions in these states mostly fall to the state comptroller.

Election history
2026
- See also: State executive official elections, 2026
Fourteen states are holding elections for auditor in 2026:
2025
- See also: State executive official elections, 2025
No state held elections for auditor in 2025.
2024
- See also: State executive official elections, 2024
Eight states held elections for auditor in 2024:
2023
- See also: State executive official elections, 2023
Two states held elections for auditor in 2023:
2022
- See also: State executive official elections, 2022
Fifteen states held elections for auditor in 2022.
See also
- State Auditor reports
- Comprehensive Annual Financial Report (CAFR)
- State executive official elections, 2024
- State executive official elections, 2025
- State executive official elections, 2026
External links
Footnotes